Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC) as an Essential Advanced Model to Express Kidney Drug Transporters and Toxicity
The benefits of using SA7K, an RPTEC clone:
- Functional uptake and efflux transporters, including OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MDR1, MRP2, MRP4, MATE1, and MATE2K
- Validated with known nephrotoxins
- Compatible with 3D models for toxicity studies
- Robust growth characteristics
- Reproducible results
Figure 1.Human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTECs) are commonly used to predict human renal drug permeability and to investigate drug efflux. We have generated transporter knockout (KO) cell lines using CompoZr® Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN) technology in a proprietary renal proximal tubule epithelial cell line.
RPTEC Drug Transporter Models and Applications
Human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTECs) are commonly used to predict human renal drug permeability and to investigate drug efflux. However, current methods for investigating drug-transporter interactions involve inhibitors or knockdown methods that are often nonspecific or inefficient. To address this, we have created RPTEC drug transporter knockout (KO) models using CompoZr® Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN) technology. CompoZr® ZFNs are a fast and reliable way to manipulate the genome in a highly specific and precise fashion. RPTEC transporter KO cell lines eliminate the ambiguity from nonspecific substrates and inhibitors, providing a more accurate and predictive model for drug-transporter interactions.
The functional activities of both OCT2 and OAT1 and OAT3 transporters were assessed in the RPTEC SA7K clone. The OCT2 substrates included amantadine, N-methylphenylpyridinium (MPP), triethylamine (TEA) and YM155. Doxepin and verapamil were used as inhibitors. For OAT1 and OAT3 transporters, substrates included 6-carboxyfluorescein (6-CF) and p-aminohippurate (PAH), and probenecid was used as the inhibitor. Activity of both OCT2 and OAT1 and OAT3 transporters was observed in the presence of an appropriate extracellular matrix (ECM) (Figure 2). In support of the importance of culture conditions for these assays, increased expression levels of mRNA for several key drug transporters in SA7K cells were observed when cultured on fibronectin-coated plates with an ECM overlay (Figure 3).
Drug Transporter Uptake Results
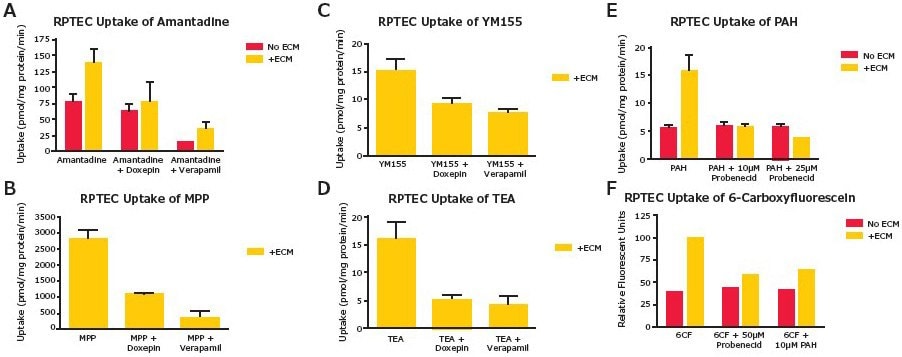
Figure 2.SA7K transporter function assays. Assays were performed in 24-well plates with or without ECM. Inhibitors were pre-incubated for 10 minutes before adding substrates. After incubating for 10 minutes, uptake was measured by LC-MS/MS.
A-D. OCT2 Transporter: All test compound concentrations (substrates and inhibitors) were 10 μM. E-F.
OAT1 and OAT3 Transporter: Substrate concentrations were 10 μM for PAH and 50 μM for 6-CF. Inhibitor concentrations were as indicated in the respective panel.
Gene Expression of Key Drug Transporters
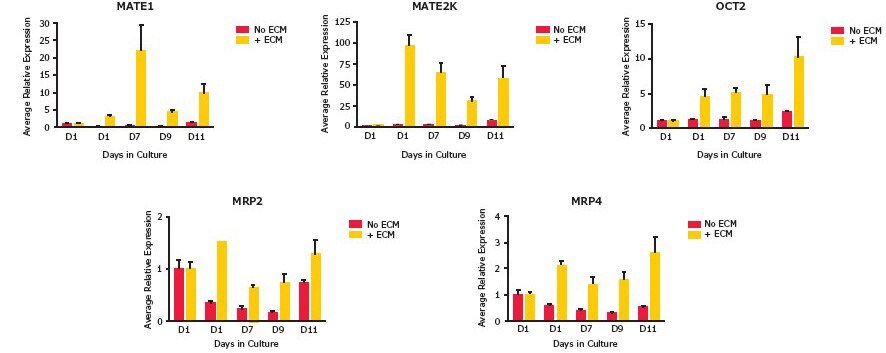
Figure 3.Enhanced gene expression in the presence of ECM overlay. Gene expression analysis by qRT-PCR showed increases of up to 20X for MATE1, 100X for MATE2K, 10X for OCT2, 1.5X for MRP2 and 3X for MRP4 transporters over the course of incubations up to 11 days.
3D Kidney Model Applications
The proximal tubule is a major target for drug toxicity that needs to be evaluated during the drug development process. We have developed functional 3D-perfused proximal tubule models with advanced renal epithelial characteristics that can be used for drug-screening studies for kidney toxicity. Nephrotoxicity assays, barrier integrity, viability assays, and imaging can be performed in as fast as one week using RPTEC SA7K cells seeded on a validated 3D cell culture platform (Figure 4).

Figure 4.Example workflow for a nephrotoxicity assay using RPTEC SA7K cells on the Mimetas OrganoPlate® 3-Lane 3D cell culture plate.
Nephrotoxicity Model on the Mimetas OrganoPlate® 3-lane 3D cell culture plate
- Form functional, polarized renal tubules for a human kidney-on-a-chip model
- Assess the effects of nephrotoxic compounds on 40 parallel cultured renal tubules formed using the human RPTEC SA7K cell line
- Create multiplexed non-invasive (viability) assays in a microfluidic format
- Use the OrganoPlate® cell culture plate with most plate readers, microscopes, and robotic handling equipment
Kidney Model on the AIM Biotech Cell Culture Chip:
- Form a polarized tubule of RPTEC SA7K cells with low permeability
- Assay compounds for nephrotoxicity through barrier integrity assays
- Design functional renal clearance assay in 3D
- Perform easy fluorescent imaging enabled by an optically clear chip design
- Perform assays under static conditions, no additional equipment or pump is required
RPTEC Media and Supplements
- Optimized for culturing RPTEC control and KO cell lines
- Easy media preparation – just thaw, mix, and use
- Superior performance and consistent results in assays for nephrotoxicity and transporter activity
- Compatible with both 2D and 3D cultures
Mimetas OrganoPlate® 3D Cell Culture Platforms
AIM Biotech 3D Cell Culture
RPTEC Media
RPTEC Cell Line Models
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?