Duolink® PLA Applications
With Duolink® PLA, you can detect, quantify, and visualize protein-protein interactions, post-translational modifications, and low expression protein detection with an easy-to-execute immunodetection protocol that is similar to traditional IF or IHC experiments, but yields far more sensitive signals. Explore the different applications below to learn more about the versatility of the Duolink® PLA products.
Protein-Protein Interaction
Post-Translational Modification
Low Abundant Proteins
Protein Localization
Digital Quantification
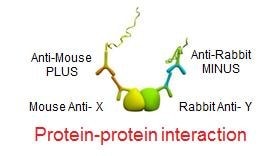
Protein-Protein Interaction
Many important biological processes are determined by protein complexes of protein-protein interactions, including - DNA replication, transcription, translation, splicing, secretion, cell cycle control, signal transduction, and intermediary metabolism. The role and activity of proteins are often modified by interactions with other proteins. Research on how proteins interact with various components of the cell is driven by the fundamental interest in understanding disease pathways. Whether protein-protein interactions are transient or stable it is critical to measure the change. Using Duolink® you can visualize stable, weak, and transient endogenous protein interactions.
To see what your protein interacts with, check out the STRING Database.
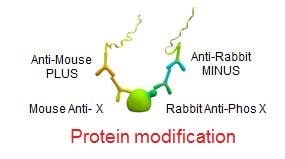
Post-Translational Modification
Interaction of proteins often depends on modification states of one or both proteins. Post-translational modifications (PTM) refer to covalent and generally enzymatic modifications of proteins during protein synthesis after its translation by ribosomes is complete. A few types of PTMs that modulate functional and structural proteomic research include – phosphorylation, glycosylation, acylation, sulfation, and ubiquitination. Historically analyzing PTMs required multiple technologies including gel electrophoresis, mass spectrometry, HPLC and immunochemistry. Duolink® enables you to visualize endogenous modification events within fixed cells and tissues.
Learn more about Post Translational Modification HERE
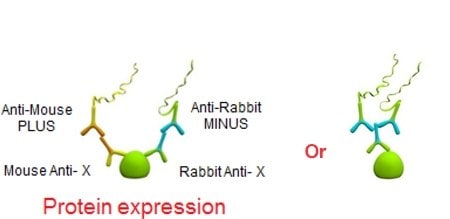
Low Abundant Proteins
Studying proteins in their native state is critical for true disease biology research. However, protein concentrations within a given sample can have a wide dynamic range. Traditionally, studying proteins in their native state resulted in having to over express the protein of interest, tagging, or genetically modifying the protein of interest. With Duolink® you can detect endogenous protein levels of a single protein or protein-protein interaction.
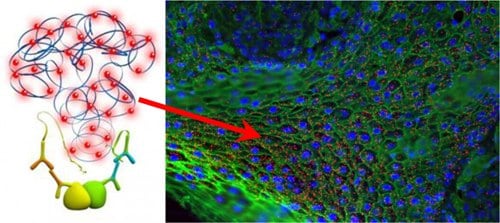
Protein Localization
Protein localization involves the computational prediction of where a protein resides in a cell. Understanding the localization of proteins at a subcellular level leads to a better understanding of protein function, how they interact, and cellular signaling pathways. Traditional technologies allow the study of endogenous protein localization, which often show off-target binding and cross-reactivity with other proteins. Duolink® enables a secondary antibody system to increase specificity and sensitivity of your protein of interest.
Digital Quantification
Both cells and tissue images may be analyzed. Most microscope software and other free software (e.g BlobFinder, Image J, Cell Profiler, etc.) can be used to analyze PLA data. When available, features such as automatic detection of nuclei and estimation of cytoplasm size allow for single cell statistical analysis of expression levels in tissue or cell populations.
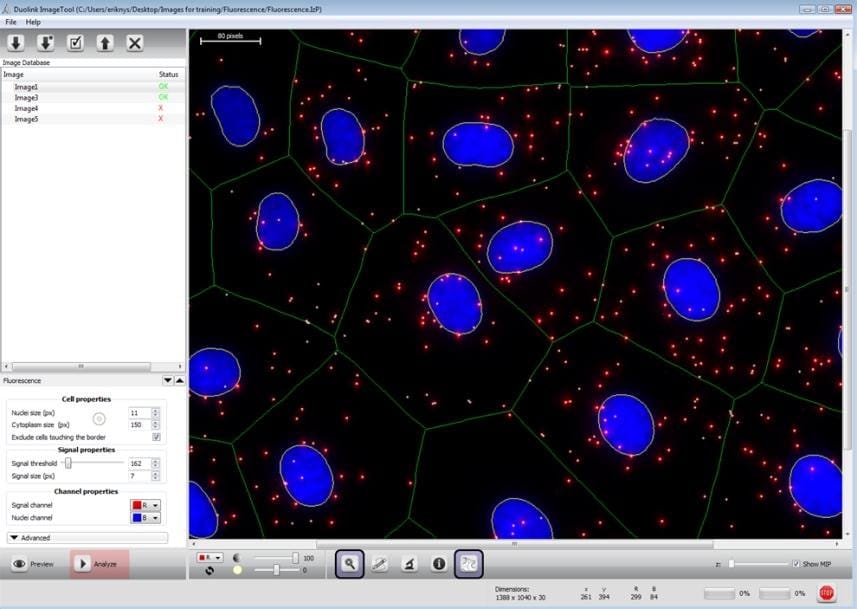
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is an excellent method for cell population analysis. Duolink® flowPLA Detection Kits will enable greater cell population analysis with its sensitive detection of proteins, protein-protein interactions, and protein modifications. To perform a Duolink® flowPLA experiment, you will need fixed, suspended cells, two primary antibodies that specifically recognize your proteins of interest, a pair of PLA probes (one PLUS and one MINUS), wash buffer, and a Duolink® flowPLA Detection Kit. The flowPLA Kits are available with 4 different fluorophores: Red, Green, Orange, or FarRed.
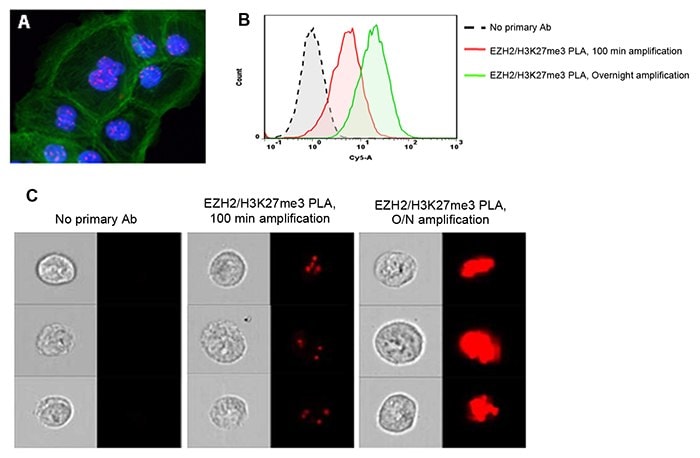
Increased amplification time during Duolink® PLA can aid in the detection of low-abundant protein targets by flow cytometry. Duolink® PLA was performed to detect the trimethylation of lysine 27 on histone 3 (H3K27me3) mediated by EZH2. A) Few PLA signals (red) in the nuclei (blue) of DU145 cells were detected by fluorescence microscopy after 100 min amplification. FITC- Phalloidin-stained actin (green) was used as a counterstain. B) Extended amplification times enhanced the detection of low-abundant protein events, such as EZH2-H3K27me3 interactions, by conventional flow cytometry. C) Combining Duolink® PLA with imaging flow cytometry allows localization of proteins or protein events (interactions or modifications) in large cell populations.
Materials
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?