Calibration, Qualification & Validation
Reference materials are substances having homogenous and well-established values of one or more properties. They play a vital role in ensuring accuracy of measurements through method calibration, validation of a measurement method, estimation of measurement uncertainty, or assigning values to materials.
They are a critical component of analytical testing workflows and broader quality assurance schemes. Manufactured under stringent requirements, reference materials differ from other lab reagents in their certification and traceability of the data provided. The world of reference materials is vast and includes Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) and other quality grades of reference materials and concepts like certificates of analysis and metrological traceability.
Featured Categories
Easily determine water content in solids, liquids, gases using Aquastar® reagents. Accurate results with our water standards for titrations.
Our analytical standards of proteins, peptides, and amino acids offer accurate and reliable results in biomarker discovery, pharmaceutical research, clinical and diagnostic testing, top-down and bottom-up proteomics, and food authentication applications.
Explore certified microbiological reference materials: VITROIDS™, LENTICULE® discs by Supelco®. Ideal for food, beverage, cannabis testing. Order today.
Certified Reference Materials are indispensable for the exact titer determination in general and Karl Fischer Titrations. They are also important for the exact calibration of analytical instruments like pH meters, AAS – Atomic Absorption Spectrometers, ICP – Inductively Coupled Plasma Spectroscopy, HPLC – High Performance Liquid Chromatography, LC - Liquid Chromatography, GC- Gas Chromatography and IC – Ion Chromatography.
Reference materials are a critical component of analytical testing workflows and broader quality assurance schemes. They are manufactured under stringent requirements and differ from other laboratory reagents in the certification and traceability of the data provided. From Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) and other quality grades of reference materials to certificates of analysis, metrological traceability, and other concepts, the world of reference materials is vast, and at times, confusing.
Reference materials are classified into five major categories based on their quality grades, from national metrology and other primary standards to Certified Reference Materials (CRMs), Reference Materials (RMs), Analytical Standards, and research grade or research chemicals. The certification and traceability requirements increase from one quality grade to the higher one. The top-level is given standardization by the national governments, whereas specific ISO guidelines provide standardization for CRMs and RMs. These ISO requirements include ISO 17034, ISO/IEC 17025, and ISO Guide 31.
Reference material producers must meet these ISO requirements to manufacture CRMs or RMs. For Certified Reference Materials, a Certificate of Analysis must be provided, and the information contained within is defined by the earlier mentioned ISO guidelines. The quality specifications for the last two levels are outlined by each independent producer rather than by a national government or ISO accreditations specific to CRMs and RMs.
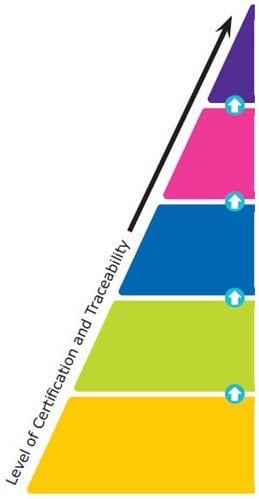
National Metrology Standard (e.g. NIST, JRC, NMI Australia)
Compendial Standard (e.g. USP, EP, BP, JP, IP)
- Issued by an authorized body
- Considered to provide the highest level of accuracy and traceability
Certified Reference Material (CRM) (ISO 17034, 17025)
- Considered to provide the highest level of accuracy, uncertainty, and traceability to an SI unit of measurement
- Manufactured by an accredited Reference Material Producer
Reference Material (RM) (ISO 17034)
- Fulfilling ISO requirements which are less demanding than for CRMs
- Manufactured by an accredited Reference Material Producer
Analytical Standard (ISO 9001)
- Certificate of Analysis available
- Level of certification varies
Reagent Grade / Research Chemical
- May come with a Certificate of Analysis
- Are not characterized for use as reference materials
Figure 2. The Hierarchy of Reference Materials - What Are the Different Types?
Depending on the method requirements or product availability, reference materials are used in three different formats ‒ powder, solution, or matrix. Selection of the right reference material is of critical importance to a laboratory’s testing application, since results are only as accurate as the reference.
Selection of reference materials based on testing purpose
The qualification and calibration of instruments require the maintenance and establishment of its traceability. The selected reference material helps a laboratory to achieve this. In daily routine system suitability applications, it might be important to qualify a reference material which is practical and easy to use, yet reliable and cost-effective for everyday use. In method validation, the use of highly accurate and precise reference materials is critical to show that the laboratory method is accurate and precise. For identity and screening purposes, important attributes of reference materials include proven authenticity and identity. In applications involving quantitation, assays, or stability assessments stable and accurate reference materials are required.
The selection of Fit-for-purpose reference materials can depend on several factors such as regulatory requirements, availability, type of testing application, level of accuracy, and sample matrix.
Visit our document search for data sheets, certificates and technical documentation.
Related Articles
- Control elemental impurities in drug products with analytical methods and materials to ensure patient safety.
- Reference materials, standards and certified reference materials are critical for analytical testing. We can help you to choose the ideal reference material for your application, whether you are using reference materials for calibration or quantitative analysis.
- The titer determination or standardization of a titration solution is essential for accurate and reliable titration results.
- NMR reference standards ensure proper instrument performance. Review key operational parameters for these standards such as pw90, sensitivity, resolution and line shape.
- Introduction of 19F qNMR certified reference materials for complex molecule certification.
- See All (63)
Related Protocols
- AOCS and AOAC methods for determining the trans fatty acid composition of foods by gas chromatography require the use of a highly polar cyanosilicone capillary column to provide the best peak resolution attainable of the numerous geometric (cis & trans) and positional isomers.
- Learn more about Neonicotinoids - active substances used in plant protection products to control harmful insects.
- Aldehydes and ketones are ubiquitous air pollutants. Along with esters and ethers, they are major components of indoor air pollution and are therefore important for industrial hygiene applications.
- Alkylphenols are used in various industries like paper manufacturing and pesticide formulations.
- IFRA method introduces new CRMs for allergenic fragrances, analyzed by GC with ionic liquid capillary column for selectivity.
- See All (63)
Find More Articles and Protocols
How Can We Help
In case of any questions, please submit a customer support request
or talk to our customer service team:
Email custserv@sial.com
or call +1 (800) 244-1173
Additional Support
- Chromatogram Search
Use the Chromatogram Search to identify unknown compounds in your sample.
- Calculators & Apps
Web Toolbox - science research tools and resources for analytical chemistry, life science, chemical synthesis and materials science.
- Customer Support Request
Customer support including help with orders, products, accounts, and website technical issues.
- FAQ
Explore our Frequently Asked Questions for answers to commonly asked questions about our products and services.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?