Choosing Correct Reference Material Quality Grade
Section Overview
- Quality Grades, Certificates of Analysis, and Metrological Traceability and What They Mean For You
- Metrological Traceability And SI Units Of Your Reference Materials
- ISO 17034 and Quality Grades of Standards, Reference Materials And Certified Reference Materials
- What Is Measured In Each Grade Of Reference Materials?
- Understanding your Reference Material Certificate of Analysis
- Reference Materials Formats–Do You Need A Neat, Solution Or Matrix Materials?
- Choose the Correct Reference Material For Your Testing Purpose
- Which Quality Grade Is The Best Fit For Your Purpose?
Quality Grades, Certificates of Analysis, and Metrological Traceability and what they Mean for You
Who Uses Reference Materials?
Reference materials are a critical component of the analytical testing workflow. Through calibration of measurement systems, validation of methods, and quality control programs, reference materials ensure accuracy in testing. From certified reference materials (CRMs) and other quality grades of reference materials, to certificates of analysis, metrological traceability and other concepts, the world of reference materials is vast, and at times, confusing.
These charts present critical reference material topics, offering information on metrological traceability, the hierarchy of reference materials, certificates of analysis, reference material formats and uses, and fit-for-purpose selection considerations. Proper selection of the right reference material for the laboratory’s testing application is important, because results are only as accurate as your reference.
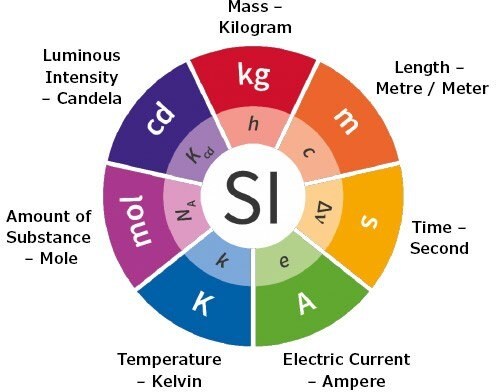
Figure 1. Metrological Traceability
Metrological traceability is an important concept in the world of reference materials. A fundamental term in metrological traceability is the SI unit of measurement. The International System of Units, or SI, defines the seven units of measure as the basic set from which all other SI units can be derived. The two most common SI units of measure for traceability of reference materials are kilogram and mole.
Metrological traceability means measurements can be meaningfully compared, across difference places, at different times, by different people, using different equipment.
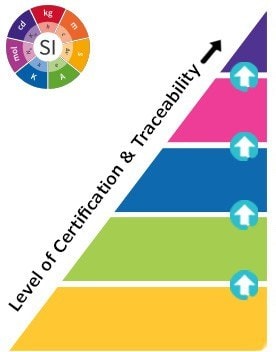
Figure 2. The Hierarchy of Reference Materials - What are the Different Types?
National Metrology Standard (e.g. NIST, JRC, NMI Australia)
Compendial Standard (e.g. USP, EP, BP, JP, IP)
- Issued by an authorized body
- Considered to provide the highest level of accuracy & traceability
Certified Reference Material (CRM) (ISO 17034, 17025)
- Considered to provide the highest level of accuracy, uncertainty, and traceability to an SI unit of measurement
- Manufactured by an accredited Reference Material Producer
Reference Material (RM) (ISO 17034)
- Fulfilling ISO requirements which are less demanding than for CRMs
- Manufactured by an accredited Reference Material Producer
Analytical Standard (ISO 9001)
- Certificate of Analysis available
- Level of certification varies
Reagent Grade / Research Chemical
- May come with a Certificate of Analysis
- Are not characterised for use as reference materials
The reference material hierarchy includes five major quality grades, from national metrology and other primary standards to Certified Reference Materials (CRMs), Reference Materials (RMs), Analytical Standards, and research grade or research chemicals. Level of certification and traceability requirements increase for each higher level. Where national governments give standardization to the top level, specific ISO guidelines provide standardization for CRMs and RMs. These ISO requirements include ISO 17034, ISO/IEC 17025 and ISO Guide 31.
Reference material producers must meet these ISO requirements to manufacture CRMs or RMs. For both of these quality grades, Certificates of Analysis must be provided, and the information contained within is defined by the aforementioned ISO guidelines. The quality specifications for the last two levels are defined by each individual producer rather than by a national government or ISO accreditations specific to CRMs and RMs.
What is Measured in Each Grade of Reference Material?
Purity and Identity of the material are typically included in the Certificate of Analysis for each of the five quality grades. Content and Stability are required for the primary standards or ISO-defined CRM and RM.
Analytical standards and research chemicals may or may not include these two parameters as their inclusion is dependent on the producer. Analytical Standards can also in some cases be Quality Control materials compliant with ISO Guide 80.
Homogeneity is required for the primary standards, CRM, and RM, but this parameter will not be found with the lower quality grades. Uncertainty and Traceability information are limited to just the primary standards and CRM. In the pharmaceutical world, secondary standards can be CRMs or RMs, but here, there are two different types of traceability – to the SI unit of measurement for the ISO-defined CRM as well as traceability to the primary compendial standard, which is a requirement specific to pharmaceutical secondary standards.
With the Certified Reference Material (CRM) or Reference Material grade comes the Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Within the CoA, there are several quality parameters which are critical to understand: accuracy, consistency, homogeneity, purity, and stability. Also, what is being certified is important to understand – namely, the certified property value, whether a concentration, potency or content.
Be sure to examine the CoA for the producer’s quality systems, the reference material’s certification process, and supporting information on traceability for a CRM. The CoA is important since it can give the laboratory information which ensures the reference material’s certification is fit for purpose within the testing method or application

Accuracy
Comparison to a primary source or certified second source – curve/calibration standard. Comparison of multiple independent preparations.
Consistency
Lot-to-lot consistency verified by comparing to the previous lot.
Stability
Expiration date established though real-time stability studie.
Homogeneity
Across the batch of ampoules/vial.
Purity
Consistent with the neat material. No contamination or degradation.
Reference Material Formats – Do you Need a Neat, Solution or Matrix Material?
Reference materials can be used in different formats in the testing laboratory, depending on product availability and method requirements. The three formats for reference materials are a neat or powder form, in solution, or matrix. The Supelco® family of reference materials includes CRMs, RMs, or Analytical Standards in each format depending on the testing laboratory’s need and testing application.
Choose the Correct Reference Material for Your Testing Purpose
For instrument qualifications and calibrations, establishing and maintaining traceability is critical. The selected reference material should help the laboratory achieve this. In daily routine system suitability applications, it might be important to qualify something that is practical and easy to use, yet reliable and cost effective for everyday use. In method validation, it’s critical to use highly accurate and precise materials to show that the laboratory method is accurate and precise. For identity and screening purposes, important attributes of reference materials include proven authenticity and identity. For quantitation, assays, or stability assessment, stable and accurate reference materials are needed.
Estimation of Uncertainties and the Use of Reference Materials (EURM): A Course from the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission
The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre has launched a free educational tool on the selection and correct use of reference materials. Critical learning objectives among the 8 modules include:
- Understand the basic concepts of uncertainty and metrological traceability.
- Learn how to use reference materials for the estimation of measurement uncertainty and how to establish the metrological traceability of measurement results.
- Learn how to select the optimal reference material.
- Understand the requirements of ISO/IEC 17025.
- Get practical tips on how to best use a reference material.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?