Western Blotting

Western blotting is a well-established analytical technique for detecting, analyzing, and quantifying proteins. This method is widely used to detect specific protein molecules in complex samples such as tissue homogenates and cell lysates. Western blotting typically involves protein separation by gel electrophoresis followed by transfer to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) or nitrocellulose membrane. After proteins have been transferred, they can be stained for visualization and directly identified by N-terminal sequencing, mass spectrometry or immunodetection.
Featured Categories
Choose from a variety of Immobilon® PVDF membranes for optimal Western blotting and protein immunoblotting performance based on target protein size, application, detection method, and convenience.
Elevate life science research with enzyme-based protein detection tools. Dive into our array of substrates & enzymes driving ELISA, IHC, WB, & beyond.
Precast polyacrylamide protein gels, running buffers, and hand-casting reagents for hand-pouring polyacrylamide gels for PAGE and SDS-PAGE protein gel electrophoresis.
In Western blotting immunodetection, proteins are identified through their binding to specific antibodies. Typically, a primary antibody is used in combination with an HRP- or AP-conjugated secondary antibody for chemiluminescent or colorimetric detection using an appropriate substrate. Alternatively, a fluorescently labeled primary or secondary antibody can be used for direct visualization.
Western blotting is used extensively in biochemistry to detect the presence of specific proteins, to determine the extent of post-translational modifications, to verify protein expression in cloning applications, to analyze protein and biomarker expression levels, in antibody epitope mapping, and to test for markers of disease in clinical settings.
The need to simultaneously analyze more proteins in limited samples has driven ongoing research into improving the sensitivity and speed of blotting techniques. Double blotting eliminates false positives caused by nonspecific interactions. Far-Western blotting enables the detection of specific protein-protein interactions. Southwestern blotting is used to identify proteins that interact with specific DNA sequences. Multistrip blotting increases throughput while minimizing inter-blot variability. New technologies are being developed to reduce the amounts of protein required to produce a signal and improve the quantitative capabilities of Western blotting.
Workflow
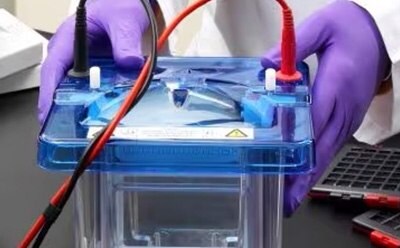
Gel Electrophoresis
Protein gel electrophoresis is used to separate and resolve proteins prior to blotting. The prepared protein mixture is run on a polyacrylamide gel to sort proteins by molecular weight and charge.
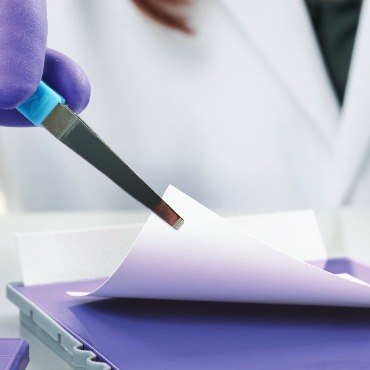
Transfer to a Membrane
The proteins separated on the gel by electrophoresis are immobilized by transfer onto a PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane. The transfer uses electric current to pull proteins from the gel onto the membrane (electroblotting).
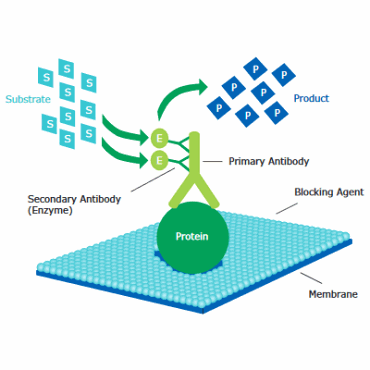
Detection
Target protein is detected using a primary antibody in combination with an HRP- or AP-conjugated secondary antibody and an appropriate chemiluminescent or colorimetric substrate, or by using fluorescently-labeled primary or secondary antibody.
Visit our document search for data sheets, certificates and technical documentation.
Related Articles
- Explore the basics of working with antibodies including technical information on structure, classes, and normal immunoglobulin ranges.
- We offer a broad range of alkaline phosphatase enzymes and substrates that are optimized for conjugation to antibodies and other proteins for your specific application needs.
- Loading controls in western blotting application.
- Gelatin is a heterogeneous mixture of water-soluble proteins extracted by boiling skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, etc. in the water.
- Troubleshoot protein transfer issues in Western blotting by understanding causes and optimizing transfer conditions.
- See All (33)
Related Protocols
- Protocol for sample preparation for cell lysis and efficient protein extraction from cultured tissues and cells for subsequent Western blotting.
- Western blot protocol details protein transfer from gels to nitrocellulose, crucial for immunoblotting procedures in research.
- BCIP/NBT substrate produces stable, intense color for alkaline phosphatase assays, ideal for visual observation.
- This page describes chemiluminescence detection of GST-tagged proteins with Amersham ECL, Amersham ECL Prime, and Amersham ECL Select from Cytiva.
- The SNAP i.d. 2.0 Protein Detection System is the second generation of the SNAP i.d. method for detecting immunoreactive proteins on Western blots.
- See All (15)
Find More Articles and Protocols
How Can We Help
In case of any questions, please submit a customer support request
or talk to our customer service team:
Email custserv@sial.com
or call +1 (800) 244-1173
Additional Support
- Chromatogram Search
Use the Chromatogram Search to identify unknown compounds in your sample.
- Calculators & Apps
Web Toolbox - science research tools and resources for analytical chemistry, life science, chemical synthesis and materials science.
- Customer Support Request
Customer support including help with orders, products, accounts, and website technical issues.
- FAQ
Explore our Frequently Asked Questions for answers to commonly asked questions about our products and services.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?