Introduction to SDS-PAGE - Separation of Proteins Based on Size
Polyacrylamide gels are formed by the reaction of acrylamide and bis-acrylamide (N,N’-methylenebisacrylamide) that results in highly cross-linked gel matrix. The gel acts as a sieve through which the proteins move in response to the electric field. Proteins contain an overall positive or negative charge; this enables the movement of a protein molecule towards the isoelectric point at which the molecule has no net charge. By denaturing the proteins and giving them a uniform negative charge, it is possible to separate them based on the size as they migrate towards the positive electrode.
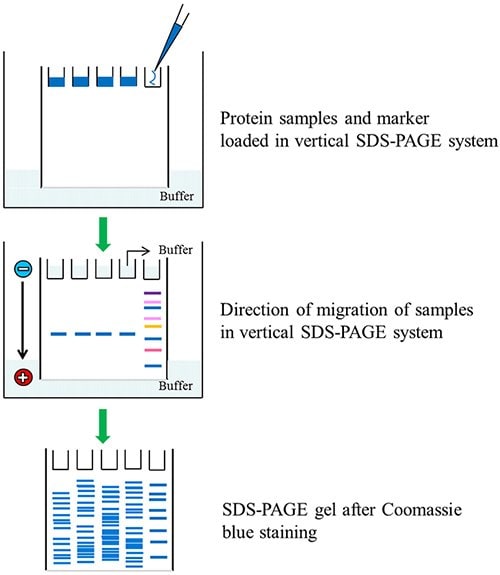
Figure 1.SDS-PAGE of protein samples and color burst protein marker(C1992)
Protocol
Materials and Reagents Required
- Vertical electrophoresis chamber with power supply, glass plates, spacers and combs
NOTE: Acrylamide and bis-acrylamide are neurotoxic in nature. All the steps should be performed wearing powder-free gloves.
Gel Preparation
- Clean the glass plates and spacers of the gel casting unit with deionized water and ethanol.
- Assemble the plates with the spacers on a stable, even surface.
- Prepare resolving gel solution using the following volumes (for 10 mL) depending on the percentage of gel required.
- Pour the gel solution in the plates assembled with spacers. To maintain an even and horizontal resolving gel surface, overlay the surface with water or isopropanol (I9516).
- Allow the gel to set for about 20-30 min at room temperature.
- Prepare stacking gel solution using the following volumes (for 10 mL):
*TEMED must be the last ingredient added
- Discard the overlayed water or isopropanol on the resolving gel
- Add the 5% stacking gel solution until it overflows. Insert the comb immediately ensuring no air bubbles are trapped in the gel or near the wells.
- Allow the gel to set for about 20-30 min at room temperature.
Sample Preparation
- To a volume of protein sample (cell or tissue lysate), add equal volume of loading buffer.
- Boil the above mixture at 95 °C for 5 min. Centrifuge at 16000 xg for 5 min.
- These samples can be stored at -20 °C or may be used to proceed with gel electrophoresis.
Gel Staining
Coomassie Blue staining: Staining of protein gels with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 is a common procedure to visualize proteins resolved by SDS-PAGE. It is highly sensitive and is suitable for long-term storage of the gels.
Reagents Required
- Gel Fix solution (500 mL)
Methanol (M3641) 250 mL
Glacial acetic acid (695092) 50 mL
Water 200 mL
- Coomassie solution
CBB R-250 (B6529) 0.1%
Methanol (M3641) 40%
Glacial acetic acid (695092) 10%
Filter the stain solution using Whatmann No. 1 filter paper.
- Destain solution
Methanol (M3641) 50 mL
Glacial acetic acid (#695092) 35 mL
- Gel storage solution
Glacial acetic acid (695092) 25 mL
Water 475 mL
Procedure
- After the electrophoresis, place the gel in a plastic tray containing gel fix solution. Place the tray on a rocking table and fix the proteins for 2 hours.
- Remove the gel fix solution and add Coomassie solution. Place on a rocking table and stain the gel for 2-4 hours.
- After the staining step, wash the gel several times with distilled water to remove excess stain.
- Add destain solution to the gel. Place on rocking table and destain for about 4 hours till clear blue bands on clear background are visible.
- After destaining, the gels may be stored in gel storage solution and photographed as required.
Silver Staining
We offer a highly sensitive protein detection silver stain kit suitable for SDS-PAGE gels. The following reagents are additionally needed:
- Fixing solution
Ethanol (E7023) 50 mL
Acetic acid 10 mL
Water 40 mL
- 30% ethanol (E7023) solution
Procedure
- After electrophoretic run immerse the gel in fixing solution for 40 min. An overnight immersion in fixer will produce clearer background.
- Remove the fixing solution and wash the gel for 10 min with 30% ethanol solution followed by wash with ultrapure water for 10 min.
- Decant the water and incubate the gel in sensitizer solution for 10 min.
- Remove the sensitizer solution and wash the gel twice with water, each wash lasting for 10 min.
- Decant the water and immerse the gel for 10 min in silver solution.
- Decant silver solution and wash the gel in water for 1.5 min.
- Discard the water and immerse the gel in developer solution for 3 to 7 min.
- Add 5 mL of stop solution to the developer solution and incubate for 5 min. Remove the developer/stop solution and wash the gel in ultrapure water for 15 min.
- The gel can be photographed and also stored in fresh, ultrapure water.
For double staining, stain the gel using CBB R-250 followed by silver stain using the procedures above.
Fluorescent Stains: We offer fluorescent SYPRO and Lucy stains for protein electrophoresis. The gels can be either immersed in the fluorescent stain in dark or the gel can be mixed with cathode buffer during the electrophoresis.
The staining protocols will depend on the stain being used and may be found here:
- SYPRO® Ruby Protein Gel Stain (PDF)
- LUCY® 506 Solution (PDF)
Reversible Gel Staining
Reversible gel stains allows the user to proceed to western blotting of proteins after SDS-PAGE.
R-PROB staining: R-PROB is a unique stain that detects proteins on PAGE gels and western blots.
Reagents Required:
- Reversible Protein Detection Kit for Membranes and Polyacrylamide Gels (RPROB)
- Fixing solution (F7264)
- 10% acetic acid
- EDTA 50 mM
Procedure
- Immerse the gels post-electrophoresis in fixing solution for 20 mins. Repeat this step twice.
- Rinse the gel in water twice, each wash lasting 30 mins.
- Incubate the gel in staining solution for 20-40 mins with gentle agitation.
- Wash off excess stain in 10% acetic acid.
- For destaining, wash the gel with EDTA followed by two washes of 15 mins each in water or fixing solution.
Copper staining: To confirm the migration and separation of proteins, the gel may be stained with a reversible stain such as CuCl2.
Reagents Required
- 0.3 M CuCl2 solution
- 0.25 M Tris and 0.25 M EDTA solution
Procedure
- Rinse the gels post-electrophoresis in distilled water for a maximum of 30 min.
- Immerse the gel in 0.3 M CuCl2 solution for 10 min.
- Rinse with de-ionized water.
- The proteins can be visualized as clear zones in a blue background.
- For destaining the gel completely for western blot, wash the stained gels in 0.25 M Tris and 0.25 M EDTA solution, pH 9, repeatedly.
- Move the destained gel to transfer buffer before proceeding with the transfer setup.

Figure 2.Blotting and Vertical Electrophoresis System
Products
Reference
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?