TRC Design and pLKO.1 Vector FAQs

pLKO.1 puro sequence
MISSION® shRNA Vector Map
What restriction sites were used for cloning the shRNA sequences?
The shRNA was cloned into the AgeI and EcoRI sites. The individual hairpin sequences can be found on our website as well.
Does pLKO.1 contain WPRE?
No, the TRC1 vector, pLKO.1-puro, does not contain WPRE (Woodchuck Posttranscriptional Regulatory Element). It is contained in the TRC2 vector, TRC2-pLKO-puro. WPRE is known for its ability to enhance transcription of transgenes.
What restriction enzymes are recommended for diagnostic digests of the clone DNA?
We recommend Pvu II. Restriction digest with Pvu II results in three bands; however, clones with an additional Pvu II site in the hairpin insert will produce four bands: 2513 bp, 2325 bp, 1478 bp and 776 bp.
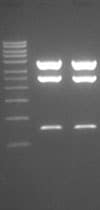
The band sizes following digestion with Pvu II of the shRNA vectors are 3803 bp, 2513 bp, and 776 bp.
How large of an insert can pLKO.1 handle?
The larger the insert put into pLKO.1 vector, the lesser the functional titer of the produced lentivirus. We generally suggest the total size of pLKO.1 be less than 9 kb.
If I order TRC1.5 clones and controls, will they work with TRC1 content?
Yes. TRC 1.5 has the same vector backbone as TRC1.
I have always ordered TRC1 products. Now, I notice that only TRC1.5 products are available. Am I getting the same products that I ordered previously?
Yes, TRC1 and TRC1.5 share the same vector backbone. TRC1.5 has all the content you love with the vector backbone you trust, now with even more coverage. TRC1.5 is the largely extended version of the old TRC1 library. All TRC1.5 controls will work with TRC1 clones.
How are TRC1 and TRC1.5 clones different?
They are not different. TRC 1.5 has the same vector backbone as TRC1. TRC1.5 has all the content you love with the vector backbone you trust, now with even more coverage. There is no difference between TRC1 and TRC1.5, except for the extended coverage.
Contact Us
For questions about the library, pricing and quotes or other concerns, please e-mail us .
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?