Analysis of 17 Cannabinoids in Hemp and Cannabis
Section Overview
- Introduction: Analysis of Cannabinoids in Cannabis and Hemp for Potency
- Sample Preparation of Standard Solutions, Peak Identification Solution, and Hemp Extract
- Preparation of Peak Identification Solution
- Chromatography
- 5.0 Conclusion: Accurate analysis of cannabinoids using HPLC
- Related Products
- Literature
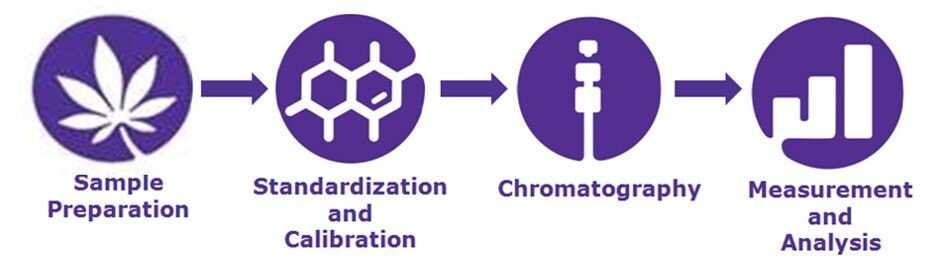
Workflow for Cannabinoid Analysis in Hemp and Cannabis
Introduction: Analysis of Cannabinoids in Cannabis and Hemp for Potency
Many countries throughout the world have started to legalize recreational and medicinal cannabis. In the United States, cannabinoid potency testing is required for cannabis and cannabis products. The Hemp plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids, and the most abundant cannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Emerging interest in the therapeutic benefits of minor cannabinoids has increased the demand for analytical methods capable of separating 17 cannabinoids. The cannabinoids targeted for testing consisted of those listed by the AOAC in standard method performance requirements (SMPRs) for dried plant material (low and high THC varieties), chocolates, and concentrates, plus three additional cannabinoids of interest.
Cannabinoid quantification can be accomplished using various analytical techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), or mass spectrometry.
A complete HPLC workflow has been developed to simplify cannabinoid profiling and potency determination. This workflow offers the following:
- Step-by-step instructions for sample preparation and analysis of 17 cannabinoids
- Rapid high-resolution gradient method: 6 minutes on C18 column (2 µm)
- Rapid gradient method: 6 minutes on C18 (2.7 µm)
- Low-pressure isocratic method: 8 minutes on C8 column (2.7 µm)
- Low flow rate for reduced solvent consumption
- Compatibility with mass spectrometry
An orthogonal analysis of a high CBD hemp strain was performed using two different stationary phases. The instructions provided below were used to prepare the hemp extract and standard solutions for cannabinoid quantitation. The Low-Pressure Isocratic and Rapid High-Resolution methods were selected to determine potency (total THC and CBD) of the hemp flower.
Chemical Structure of 17 Cannabinoids

Preparation of Mobile Phases
Preparation of Standard Solutions

Low Pressure Isocratic Method: Standard Solution and Blank
Chromatograms: Standard Solutions

Rapid High-Resolution Gradient Method: Standard Solution and Blank
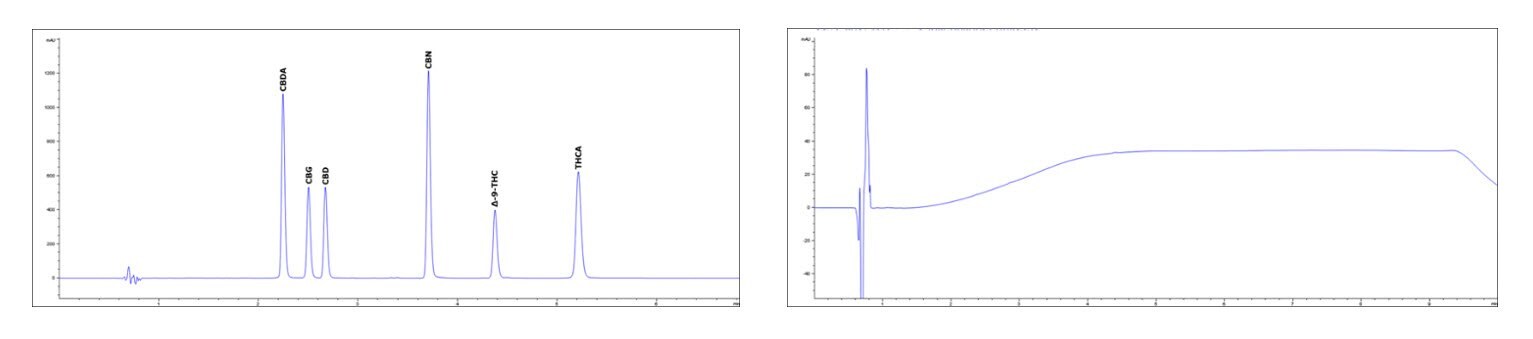
Rapid Gradient Method: Standard Solution and Blank
System Suitability: Peak Identification Solutions

Low Pressure Isocratic Method: 17 Cannabinoids in Peak Identification Solution
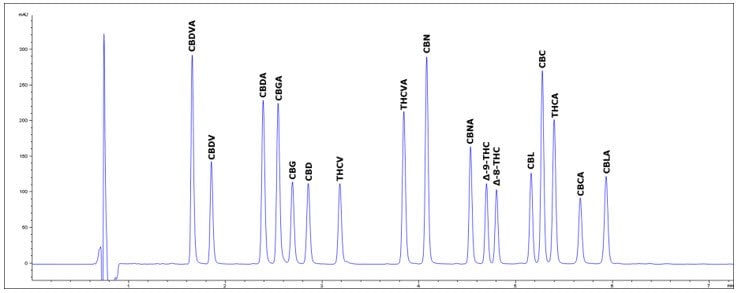
Rapid High-Resolution Method: 17 Cannabinoids in Peak Identification Solution

Rapid Gradient Method: 17 Cannabinoids in Peak Identification Solution
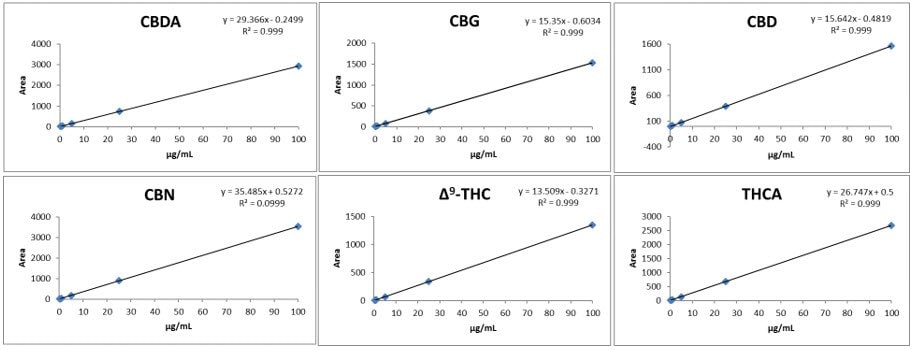
4.1 Low Pressure Isocratic Method: Linearity and Range (0.25-100 µg/mL)

4.2 Rapid High-Resolution Gradient Method: Linearity and Range (0.25-100 µg/mL)
5.0 Conclusion: Accurate analysis of cannabinoids using HPLC
A complete HPLC workflow has been developed to simplify cannabinoid profiling and potency determination. This workflow offers simple sample preparation and a choice of three methods:
- Step-by-step instructions for sample preparation and analysis of 17 cannabinoids
- Rapid High-Resolution Gradient Method: 6 minutes on C18 column (2 µm)
- Rapid Gradient Method: 6 minutes on C18 (2.7 µm)
- Low Pressure Isocratic Method: 8 minutes on C8 column (2.7 µm)
- Low flow rate for reduced solvent consumption
- Compatibility with mass spectrometry
Using the Rapid High-Resolution Gradient and the Low Pressure Isocratic Methods in an orthogonal approach, the total THC was found to significantly exceed the 0.3% total THC limit imposed by the United States Department of Agriculture Interim Final Rule. Results with the Rapid Gradient Method were comparable (data not shown). Although ∆9-THC levels were low, a significant amount of the acidic form (THCA) was present. The hemp sample tested here illustrates the challenges in hemp production to obtain results in a timely manner for harvesting before THC content exceeds regulatory requirements. Rapid and accurate methods support timely analysis of hemp and cannabis.
The results confirmed the high total CBD content, with the majority found to be in the acidic form (CBDA). The results from all methods were in agreement and demonstrated a high degree of selectivity despite the abundance of matrix components.
These methods can easily be adopted to quantitate cannabinoids in plant material spanning concentrations of 0.05–100% by weight. The short run times and low solvent use makes these methods cost-effective for high-throughput potency testing.
Related Products
Literature
- Quantitation of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Dried Plant Materials, Concentrates, and Oils Using Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detection Technique with Optional Mass Spectrometric Detection: Single-Laboratory Validation Study, First Action 2018.11
- AOAC SMPR 2017.002. Standard Method Performance Requirements (SMPRs) for Quantitation of Cannabinoids in Dried Plant Materials
- AOAC SMPR 2019.003. Standard Method Performance Requirements (SMPRs) for Quantitation of Cannabinoids in Plant Materials of Hemp (Low THC Varieties Cannabis sp.)
- AOAC SMPR 2017.019. Standard Method Performance Requirements (SMPRs) for Quantitation of Cannabinoids in Edible Chocolate
- AOAC SMPR 2017.001. Standard Method Performance Requirements (SMPRs) for Quantitation of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Concentrates
- Establishment of a Domestic Hemp Production Program
- Guidance for State Medical Cannabis Testing Programs (Association of Public Health Laboratories)
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?