Enzymatic Assay of Lyticase
Description
This procedure may be used for the determination of Lyticase activity using Baker’s yeast as the substrate. The turbidimetric rate determination [Absorbance at 800 nm (A800), Light path = 1 cm] is based on the following reaction:

Unit Definition: One unit of lyticase will produce a ΔA800 of 0.001 per minute at pH 7.5 at 25 °C, using a suspension of yeast as the substrate in a 3 mL reaction mixture.
Reagents and Equipment Required
- 1 M Potassium phosphate monobasic solution (Catalog Number P8709)
- 1 M Potassium phosphate dibasic solution (Catalog Number P8584)
- Yeast from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Catalog Number YSC1)
Precautions – Please consult the Safety Data Sheet for information regarding hazards and safe handling practices.
Preparation Instructions
Use ultrapure water (≥18 MΩxcm resistivity at 25 °C) for the preparation of reagents.
Phosphate Buffer (67 mM Potassium Phosphate Buffer, pH 7.5, at 25 °C) – To prepare 100 mL:
- Pipette 1.33 mL of 1 M Potassium phosphate monobasic solution (Catalog Number P8709) into a suitable beaker.
- Add 5.37 mL of 1 M Potassium phosphate dibasic solution (Catalog Number P8584).
- Dilute to 100 mL with ultrapure water.
- Adjust to pH 7.5 with 1 M KOH.
Substrate [0.4% (w/v) suspension of baker’s yeast (yeast from Saccharomyces cerevisiae)] –
Using a mortar and pestle grind a suitable amount of yeast (Catalog Number YSC1) to obtain greater than 800 mg of powder. The ground powder should be between 25–30 mesh size.
Using the powder, prepare a 4 mg/mL yeast suspension in ultrapure water.
Stir the solution at a speed where a minimal vortex is created. Mix for ~1 hour at room temperature.
Note: Stirring at higher speeds could cause premature lysing of the yeast cells.After 1 hour, cease stirring to allow the larger sediments to settle for 30 minutes. Carefully decant the upper two thirds of the supernatant into a new beaker. Removing the larger sediments will minimize the amount of noise seen in the spectrophotometer readings when performing the assay.
The substrate concentration must be verified prior to running the assay.
a. Pipette the following reagents into suitable cuvettes:
b. Measure the A800 of the yeast mixture versus ultrapure water. The ΔA800 [ΔA800(Substrate) = A800(Substrate) – A800(Blank)] must be between 0.7 –1.0. If necessary, adjust the absorbance using appropriate amount of yeast powder or ultrapure water.
Slowly mix the Substrate (with minimal vortex) at room temperature throughout the assay. It is stable for up to 8 hours.
Enzyme Solution – Prepare a 10 mg solid/ml lyticase solution. Immediately before use, prepare a secondary dilution so that the corrected ΔA800/min falls between 0.025 and 0.035. If the rate falls outside this range, make the appropriate adjustment to the secondary dilution and repeat.
Notes:
For some crude lyticase products it may take more than 15 minutes to go into solution. Short sonication periods of 1–15 seconds can aid in dissolving the enzyme without affecting the enzymatic activity.
If the corrected absorbance is less than 0.025 make the enzyme more concentrated to achieve corrected absorbance between 0.025-0.035.
If the corrected absorbance is more the 0.035 make the enzyme less concentrated to achieve corrected absorbance between 0.025-0.035.
Procedure
In a 3.00 mL reaction mixture, the final concentrations are 34 mM Potassium Phosphate, ~0.12% (w/v) baker’s yeast, and 25–35 units of Lyticase.
Pipette the following reagents into suitable containers:
Mix the tests and the blank cuvettes by inversion and equilibrate to 25 °C. Then add the Enzyme Solution:
Immediately mix the blank and all tests by inversion. Perform this sequentially to capture the settling effects of the substrate. Record the decrease in absorbance at A800 for ~10 minutes
Using a 2 minute time period, obtain the ΔA800/min using the maximum linear rate for each Test. Each Test rate needs to be corrected using the corresponding time frame for the Blank.
The corrected ΔA800/min must fall between 0.025 and 0.035 in order for the assay to be valid. If the rate falls outside this range, make the appropriate adjustments to the enzyme concentration and repeat.
Results
Calculations
1.

where:
df = dilution factor of enzyme
0.001 = Change in absorbance at 800 nm as per the unit definition
0.050 = Volume (mL) of Enzyme Solution used in reaction
2.
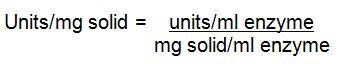
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?