Sterility Testing of Products in Isopropyl Myristate
Sterility Testing of Viscous Oils, Water-in-Oil Emulsions and Fatty Base Ointments
Membrane filtration is the pharmacopoeial method of choice for sterility testing. Viscous products, for example creams and ointments, can be difficult to filter and are therefore normally diluted in a sterile solvent such as isopropyl myristate (IPM). Testing such products may be problematic if specific testing procedures are not implemented and the appropriate devices not used. The Steritest® NEO device TZHVSL210 is the perfect choice for testing solvents, creams, ointments and veterinary injectables due to its solvent-resistant nylon canister, Durapore® (PVDF) membrane, reinforced base structure and canister connection.
This article describes one possible test set-up to dilute a product in IPM, filter it and rinse the membrane to eliminate residues that may inhibit microbial growth. Depending on the nature of the product, the method may have to be adapted to pass the necessary method suitability test (see “pharmacopoeia acceptance criteria and method suitability test” below).

Figure 1.Isopropyl Myristate and Green base Steritest® NEO filtration device (TZHVSL210).
The new Steritest® NEO device is upgraded with new improvements such as colored clamps, graduations for accurate volume measurement, optimized identification, and traceability with the new peel-off label. The test system offers an optimized and fully compliant testing process, when used with the Steritest® Symbio pump, specific accessories and high-quality culture media and rinsing fluids.
Section Overview
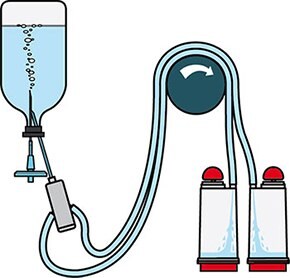
Figure 2.Schematic diagram of sterility testing using Steritest® NEO devices.
Sterility Testing Experimental Materials
- Membrane filtration device: Green base Steritest® NEO device, TZHVSL210
- Solvent: Isopropyl Myristate (IPM) sterile, ready-to-use solvent, 1466280006
- Culture media: Soybean-Casein Digest medium (TSB) (100 mL in total) and 100 mL in total of either Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (FTM) or Clear Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (CTM)
- Rinse fluids: Rinsing Fluid A (200 mL in total), Fluid K (600 mL in total).
- Double packaged media, fluids and different formats are available.
- Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) as a disinfecting agent
- Steritest® Symbio Pump for laminar flow hood or isolator.
Sterility Testing Method and Sample Preparation
The following procedure is an example of a test method that will serve as a base during method development. It should be validated afterward following the instructions mentioned in pharmacopeia before use in routine.
- Set up the system of Steritest® pump and NEO device.
- Wipe IPM and Fluid K bottles with 70% isopropyl alcohol (IPA) before placing them into the testing environment.
- Take the bottle containing IPM and transfer IPM into two empty sterile glass bottles:
- the necessary volume to dilute your product sample and
- 100 mL for pre-wetting the membrane. The transfer tool Steridilutor® Neo (TZA000010) can be used to prepare the needed IPM volume for your test set-up.
- Aseptically dispense the appropriate amount of test sample as required by USP/EP/JP into the bottle of IPM for sample dilution (bottle filled in step 3a).
- Take the Fluid K bottle and the other bottles needed (see “sterility testing experimental materials” above), one at a time, and wipe each bottle with 70% IPA before placing it in the testing environment.
- Pre-wet the membrane of each of the two canisters with 50 mL of IPM (bottle filled in step 3b).
- Filter the sample diluted in IPM that was prepared in step 4 (see above).
- Rinse each canister’s membrane three times with Fluid K. For each rinsing step, the canister is filled with 100 mL Fluid K and then filtered. When approximately 30 to 50 mL of Fluid K have passed through the membrane, gently swirl the canister to rinse residuals of IPM and sample from the canister’s sides.
Note: In our experiments, poor rinsing was observed when the membrane filter remained covered with liquid throughout the filtration and rinsing steps. To avoid this, the entire volume of diluted sample should be filtered through the Steritest® NEO devices (step 7), followed by the entire volume of each Fluid K rinse (step 8).
- Do a last rinse with 100 mL of Fluid A per membrane to remove residuals of Fluid K.
- Add 100 mL of Soybean–Casein Digest Medium (TSB) to one canister and 100 mL of Fluid Thioglycollate Medium (either FTM or CTM) to the other canister.
- Start incubation (TSB at 20 to 25 °C for 14 days; FTM/CTM at 30 to 35 °C for 14 days).
- Observe for growth/no growth.
- The test passes if no growth after 14 days of incubation can be detected. If any growth occurs during this period, the test has failed, and additional investigation should be undertaken to determine the reason of the contamination.
Pharmacopoeia Acceptance Criteria and Method Suitability Test
According to the pharmacopoeias, recovery must be tested to ascertain that the method is suitable. To do so, inoculate the last Fluid K rinse with no more than 100 CFUs of the microorganisms as recommended in the pharmacopoeias. Environmental isolates can also be tested this way. When filtration is complete, add media (TSB and either FTM or CTM) to the canisters and incubate for the time and temperature that the pharmacopoeias recommend. Then observe the canisters to see if the pharmacopoeia acceptance criteria for growth have been met.
Note: Microbiological recovery tests are performed to demonstrate the ability to detect microorganisms in the presence of IPM. If IPM is directly inoculated with microorganisms, add 9% of NaCl peptone buffer to generate an IPM/water emulsion (e.g., 9 mL NaCl peptone buffer, add microorganism suspension and fill up to 100 mL with IPM) and perform the filtration within 10 minutes to increase the survival rate of challenging microorganisms. Under these conditions recovery rates of ≥50% must be obtained.
For further reading and more information click on the links below
Method Development and Validation Services
Our team of expert engineers will assist you in implementing method development and validation within your QC microbiology lab. Additionally, you will be provided with basic and advanced technical training on sterility testing, on-site or remotely.
Rely on our expertise to support you in various situations including:
- New laboratory sterility testing equipment
- New product or reformulated product sterility testing
- Compliance with updated regulations: EP, USP, JP, etc.
- PQ consultancy after the completion of IQ/OQ
- Method development execution or consultancy
- Investigation of out-of-specification results
Related Products
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?