Analysis of Vitamin B Compound Tablets by HPLC-UV acc. to Chinese National Drug Standard Draft
Abstract
A Discovery® HS C18 HPLC column was utilized in the development of an analytical method for the quantification of five B vitamins in compound vitamin B tablets in accordance with a draft method of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The developed method fulfilled the suitability requirements of the Chinese Pharmacopeia and demonstrated adequate precision and accuracy for the quantitative determination of the vitamin B constituents in compound tablet formulations.
Section Overview
Introduction
Compound vitamin B tablets are combination formulations that generally contain vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), nicotinamide (vitamin B3), calcium pantothenate (vitamin B5), and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and are administered as dietary supplements.1,2 A public draft of the national drug standard for vitamin content determination in composite vitamin B tablets was released by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission in 2024.3 This work describes an analytical method that adheres to the specifications of the draft standard and the associated suitability criteria for determining the content of five B vitamins (Figure 1) in compound vitamin B tablets by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a Discovery® HS C18 column and UV detection.
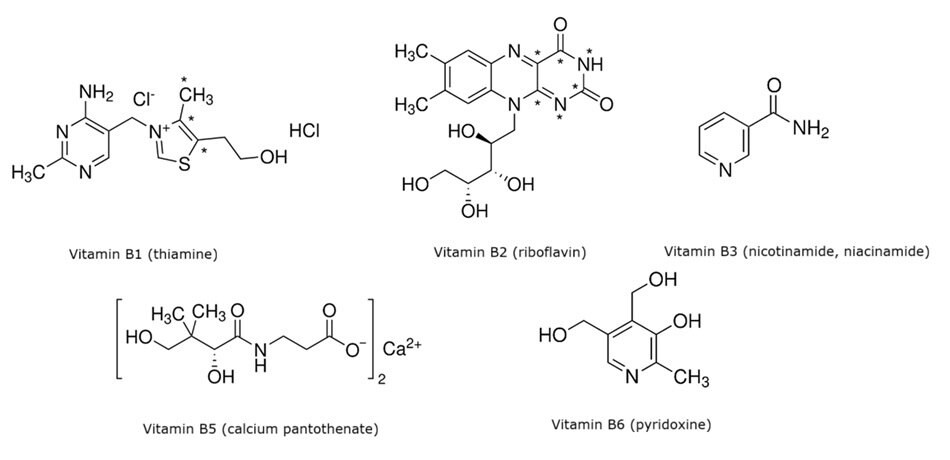
Figure 1.Chemical structures of the five B vitamins analyzed in this work.
Experimental
Mobile Phase, Standard & Sample Preparation
Mobile Phase Preparation
Mobile phase A: Dissolve 0.4 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) and 0.2 g of heptane-1-sulfonic acid sodium salt in a suitable beaker. Add 1000 mL of purified water and stir the mixture until all solids are completely dissolved. While stirring continuously, gradually adjust the pH with 85% ortho-phosphate acid(H3PO4) until it reaches pH 3.0.
Standard Preparation
- Standard stock solution 1 (Vit. B2): Accurately weigh approximately 15 mg of a vitamin B2 standard into a 50 mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in 12 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid solution, dilute with water to the mark and mix well. The resulting solution has a concentration of 0.3 mg/mL of vitamin B2.
- Standard stock solution 2 (Vit. B1, B5, B6): Accurately weigh 30 mg of vitamin B1, 80 mg of calcium pantothenate, and 16 mg of vitamin B6 standards into a 50 mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to the mark and mix well. The solution contains 0.6 mg/mL vitamin B1, 1.6 mg/mL calcium pantothenate (vit. B5), and 0.32 mg/mL vitamin B6.
- Calibration solutions 1-6: Solutions are prepared according to Table 1a. Accurately weigh approximately nicotinamide standard and transfer to a volumetric flask (volume as indicated). Add volumes of standard stock solution 1 and standard stock solution 2. Dilute with water to the mark and mix well. The solutions contain concentrations displayed in Table 1b.
Note: Calibration sample 4 represents the equivalent concentrations labeled on commercial composite tablet sample.
Sample Preparation
A commercially available compound vitamin B tablet product was employed as the test sample. The composition stated on the product label is provided in Table 8.
Tablet Sample 1 (for determination of nicotinamide, vit. B1, and B2)
- Accurately weigh 20 tablets and grind to a fine powder using a mortar and pestle. Weigh a suitable amount of the fine powder, approximately equivalent to 10 mg of nicotinamide (according to tablet product label), into a 100 mL volumetric flask.
- Add approximately 70 mL of water and subject the mixture to ultrasonic treatment in a water bath at 50 °C for 15 minutes.
- Allow the solution to cool to room temperature, then dilute and fill up with water to the mark and mix thoroughly.
- Filter the solution with 0.45 µm PVDF membrane filter and use an aliquot of the resulting filtrate as the test solution for the determination of nicotinamide, vitamin B2 and vitamin B1.
- In refence of the packaging label of the tablets the resulting sample solution should contain nominal concentrations of 30 μg/mL vitamin B1, 15 μg/mL vitamin B2, 100 μg/mL nicotinamide.
Tablet Sample 2 (for determination of calcium pantothenate and vit. B6)
- Accurately weigh 20 tablets of the sample into a 250 mL volumetric flask. Add 20 mL of water and shake gently to facilitate disintegration.
- Then, add 130 mL of water and subject the mixture to ultrasonic treatment for 15 minutes. Dilute with water to the volume mark and mix thoroughly.
- Centrifuge the solution at 8000 rpm for 15 minutes and use an aliquot of the supernatant as the test solution for the determination of calcium pantothenate and vitamin B6.
- In refence of the packaging label of the tablets the resulting sample solution should contain nominal concentrations of 80 μg/mL calcium pantothenate and 16 μg/mL vitamin B6
LC Conditions
The HPLC conditions applied for the analysis of the five analytes, namely nicotinamide, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, calcium pantothenate, and vitamin B6 in compound vitamin B tablets are described in Table 2.
Method Suitability
Acceptance criteria3:
- The theoretical plate number calculated based on the nicotinamide peak should not be less than 5,000.
- At a wavelength of 205 nm, the resolution between the nicotinamide peak and the calcium pantothenate peak should not be less than 6.0.
- Resolution between other major peaks should comply with the specified requirements (acc. to the ChP: resolution ≥ 1.5).
Results & Discussion
Specificity and System Suitability
The specificity characteristic chromatograms of the method at UV absorption wavelengths of 261 nm, 205 nm, and 290 nm for calibration solution 4 are shown in Figures 2 to 4. The data indicated that excellent method specificity was achieved, with all compounds being baseline-separated and hence clearly detected. All peaks show good symmetry with tailing factors between 0.9 and 1.1. The system suitability results obtained with the calibration solutions are displayed in Tables 3 to 5.
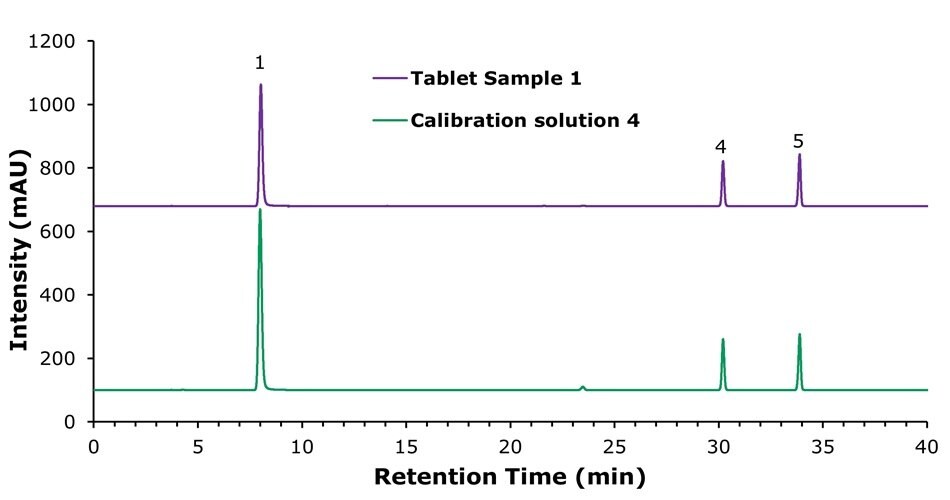
Figure 2.Chromatograms of the calibration solution 4 (bottom) and tablet sample 1 solution (top) at a detection wavelength of 261 nm for nicotinamide (1), vitamin B1 (4), and vitamin B2 (5) (concentrations are 100 µg/mL, 30 µg/mL, and 15 µg/mL, respectively, for both tablet sample 1 and calibration solution 4).
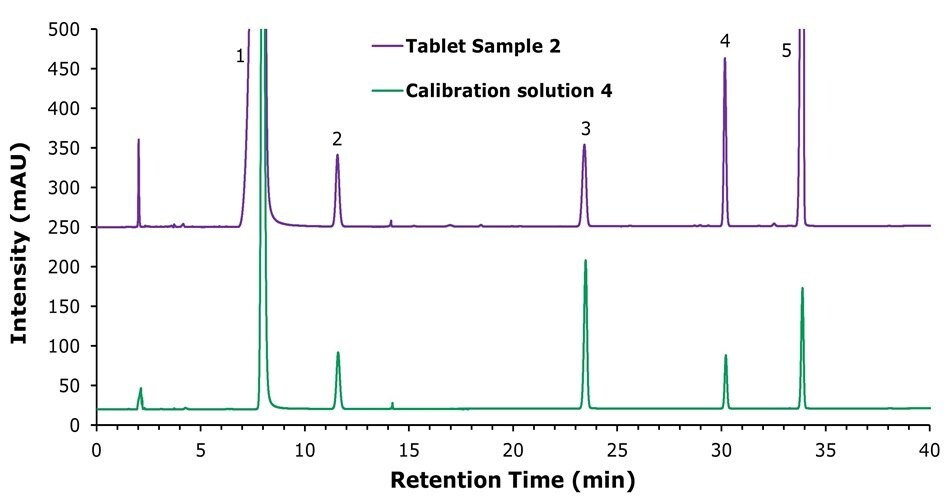
Figure 3.Chromatograms of the calibration solution 4 (bottom) and tablet sample 2 solution (top) at a detection wavelength of 205 nm for calcium pantothenate (2) at 80 µg/mL in both tablet sample 2 and calibration solution 4. (1) Nicotinamide, (3) vitamin B6, (4) vitamin B1, (5) vitamin B2.

Figure 4.Chromatograms of the calibration solution 4 (bottom) and tablet sample 2 solution (top) at a detection wavelength of 290 nm for vitamin B6 (3) at 16 µg/mL in both tablet sample 2 and calibration solution 4. (1) Nicotinamide, (4) vitamin B1, (5) vitamin B2.
The theoretical plate numbers calculated for the nicotinamide peak at wavelengths of 261 nm, 205 nm, and 290 nm were 11,724, 11,724, and 10,938, respectively, and all values therefore exceeded the required plate count of 5,000. The resolution between nicotinamide and calcium pantothenate at 205 nm was 12.1, meeting the acceptance criterium of > 6.0. All parameters were observed to exceed the system suitability requirements outlined in the draft national drug standard for composite vitamin B tablets, and the resolution of all other major peaks (for details see Tables 3 to 5) complied with the standards issued by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.4
Calibration
The calibration curve for nicotinamide is shown in Figure 5 as example. The calibration data for nicotinamide, calcium pantothenate, vitamin B6, vitamin B1, and vitamin B2 provided r values (correlation coefficient) of greater than 0.999, diplaying excelent linearity within the calibrated ranges (Table 6).
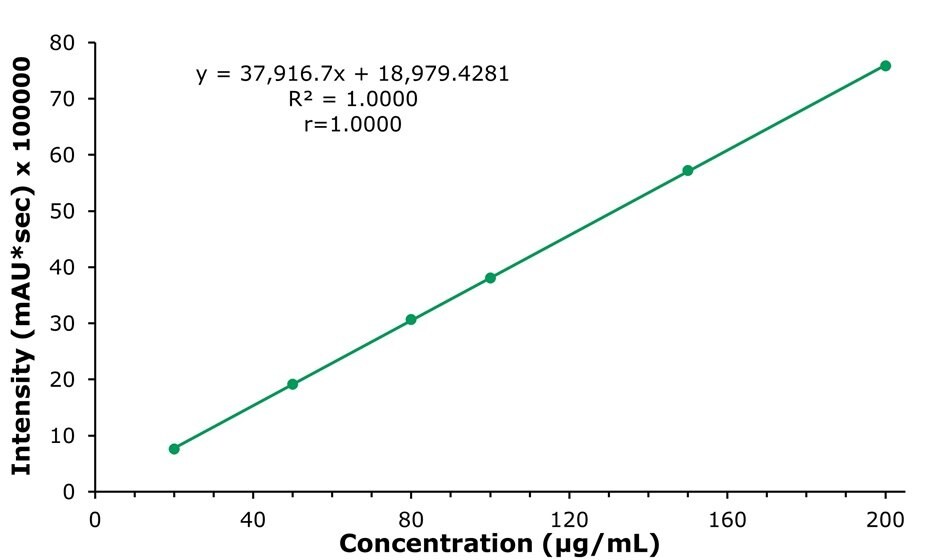
Figure 5.Calibration curve of niacinamide at 261 nm obtained by the analysis of calibration solutions. (c=20.0, 50.0, 80.0, 100.0, 150.0 and 200.0 µg/mL)
Repeatability
The repeatability of the procedure was evaluated by six consecutive injections each of tablet sample 1 and tablet sample 2. The results for nicotinamide, calcium pantothenate, vitamin B6, vitamin B1, and vitamin B2 at their respective detection wavelengths are summarized in Table 7. Good repeatability was demonstrated, with RSD% of peak areas for all analytes being significantly below 2.0%, which represents the acceptance criteria for reproducibility outlined in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia General Principles 9101.4
Tablet Sample Analysis
Utilization of the developed analytical procedure together with the established calibration enabled the assay of the compound vitamin B tablets, and the measured contents were confirmed to be consistent with the values declared on the tablet package label as shown in (Table 8).
Conclusion
An HPLC-UV method for the determination of vitamin B compounds in compound vitamin B tablets was developed utilizing the Discovery® HS C18 column in accordance a draft method of the Chinese Pharmacopeia. The calibration ranges for vitamins B1, vitamin B2, nicotinamide (B3), calcium pantothenate (B5), and vitamin B6 were 6 to 60 µg/mL, 3 to 30 µg/mL, 20 to 200 µg/mL, 16 to 160 µg/mL and 3.2 to 32 µg/mL, respectively. The method complied with the suitability criteria specified in the draft method and provided excellent linearity (r> 0.999) and reproducibility (RSD <0.06%). These observations support the suitability of the Discovery® HS C18 column for the draft method, providing required separation performance and reproducibility.
Solvents, Reagents & Certified Reference Materials
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?