Affinity Purification with Ultrafree®-MC Centrifugal Filters
Affinity interaction chromatography is an effective method for protein purification that can achieve up to 95% purity in one step. It is often employed in the small-scale batch mode as a quick method for microgram-scale protein purification. The typical protocol involves:
- Pipetting a small volume of affinity resin into the microfuge tube containing the sample
- Vortexing the tube for a few minutes
- Centrifuging the resin to the bottom
- Pipetting off the supernatant
- Washing a few times (using steps 2 and 3)
- Eluting with a small amount of eluent
Pre-packed mini-spin columns for protein purification simplify this process into a one-hour protocol.
For a more flexible protocol, centrifugal devices with a microporous membrane, such as Ultrafree®-MC centrifugal devices, hold the sample and affinity resin in a filter basket, thus creating a “home-made” mini-spin column. These devices combine the high efficiency of batch binding and washing with the handling convenience of a mini-spin column.
With minimal hands-on time, the method provides flexibility in resin-to-lysate ratio and binding conditions, independent of centrifugation speed and rotor angle. Here, the method was used to purify rabbit IgG on ProSep® resin and His-tagged C-RP protein on three different commercial metal-chelate resins.
Method for IgG Purification
Solutions
- ProSep-A binding buffer A: 1.5 M Glycine/NaOH, 3 M NaCl, pH 9.0
- ProSep-A elution buffer B2: 0.2 M Glycine/HCl, pH 2.5
- ProSep-A neutralization buffer: 1 M Tris/HCl, pH 9.0
Procedure
- 200 mg of ProSep® resin were placed in Ultrafree®-MC 0.45 μm filter basket.
- The columns were equilibrated with 400 μL of binding buffer A and centrifuged for 1 minute at 100 x g.
- 200 μL of rabbit serum were diluted 1:1 with binding buffer and the entire volume was loaded into the spin column containing PROSEP-A resin.
- Devices were placed on a shaker for 15 minutes at room temperature and centrifuged at 100 x g for 5 minutes. Flow-through was collected for future analysis.
- Three consecutive washes were performed, each time adding 400 μL of binding buffer A and centrifuging at 2,000 x g for 2 minutes.
- 200 μL of elution buffer B2 were added and centrifuged for 2 minutes at 2,000 x g.
- 26 μL of neutralization buffer were added to each collection tube. A second elution was collected after repeating the same process one more time.
Method for His-tagged C-RP Purification using Ultrafree® devices
Solutions
- Lysis buffer: 50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride, 10 mM immidazole, pH 7
- Binding buffer: 50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride, 10 mM immidazole, pH 7
- Wash buffer: 50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride, 20 mM immidazole, pH 7
- Elution buffer: 50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride, 250 mM immidazole, pH 7
- 1 mg/mL Lysozyme stock
- Benzonase
Procedure
- Express recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli.
- Prepare at a 10X concentration using lysis buffer. (Pellet 100 mL of culture, resuspend in 10 mL of lysis buffer.)
- Add lysozyme to a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL and Benzonase® nuclease to reduce the viscosity of the lysate.
- Clarify the lysate by centrifugation (10 min at 10,000 x g).
- Add 200 μL of 50% resin slurry to the Ultrafree®-MC device. Spin the device for 1 min at 500 x g to remove any residual fluid of the resin.
- Equilibrate the resin with 500 μL of binding buffer and centrifuge for 2 minutes at 500 x g.
- Add 500 μL of the clarified lysate to the resin and incubate for 30 min with light agitation.
- Spin the device at 500 x g for 10 min to remove the unbound lysate proteins.
- Wash the resin with 500 μL of wash buffer and incubate for 5 minutes with agitation. Spin the device for 5 minutes at 500 x g.
- Repeat the washing step two more times.
- Add 250 μL of elution buffer and mix for 5 minutes.
- Spin the device for 1 min at 500 x g to recover the purified protein
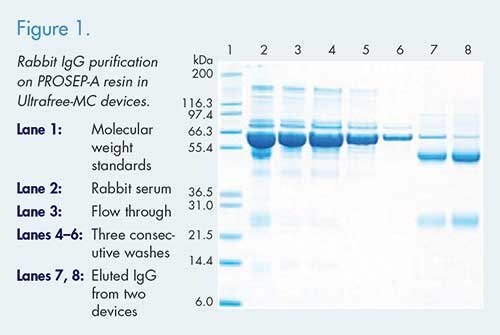
Figure 1. shows the SDS-PAGE analysis for rabbit IgG purified using an Ultrafree®-MC centrifugal device. Starting material contained approximately 14 mg of total protein, with an estimated 1.5–2 mg IgG content. The total amount of purified IgG was 1.2 mg and 1.1 mg (estimated by OD280) on two devices processed in parallel. This method can be useful for monitoring the titer of antigen-specific antibodies after immune activation, or whenever small amount of IgG is needed.
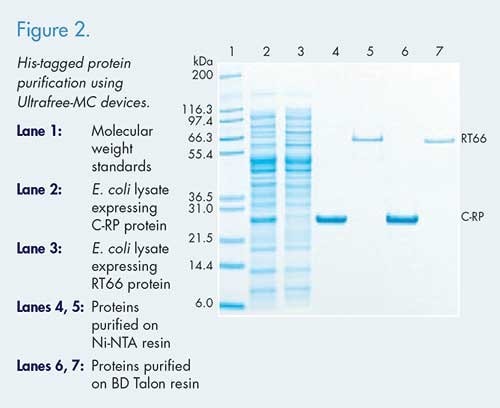
Figure 2. shows the SDS-PAGE analysis of His-tagged protein purified using an Ultrafree®-MC devices, with Ni-NTA agarose and BD Talon™ resin. From 500 μL of lysate, two recombinant proteins were purified, 32-35µg of CRP (a 26 kDa, high-expressing protein) and 8 μg of RT66 (a 66 kDa, low-expressing protein). This method is applicable to recombinant protein purification, antibody purification, and immunoprecipitation.
Materials
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?