Determination of Glycyrrhizic Acid, Honokiol and Magnolol in Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui
Abstract
This study describes the development of an HPLC method for the determination of the three active components, honokiol, magnolol, and glycyrrhizic acid, in Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui, based on a draft monograph method released by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Following sample preparation, honokiol and magnolol were analyzed using an Ascentis® Express C18 superficially porous particle HPLC column, whereas glycyrrhizic acid was determined using a Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped column designed for extended pH stability. Both methods fulfilled the requirements specified in the draft, confirming their suitability for the determination of these three active ingredients in Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui.
Section Overview
Introduction
Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui is a well-known liquid herbal formulation in traditional Chinese medicine. It has historically been used to treat various ailments, including colds caused by external wind and cold, internal disorders arising from damp stagnation, and symptoms associated with summer heat and dampness, such as headache, heaviness, chest fullness and discomfort, abdominal distension and pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and gastrointestinal-type colds.1,2
The formulation is composed primarily of traditional Chinese herbs, including Atractylodes, dried tangerine peel, magnolia bark (processed with ginger), Angelica dahurica, poria, dafupi, raw pinellia, licorice extract, patchouli oil, and perilla leaf oil, with dried ginger and ethanol serving as excipients.2,3
In 2024, the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission released a draft method for the detection of three marker components in Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui.4 Following public validation, this method is intended for inclusion in the 2025 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.
The draft method specifies honokiol, magnolol, and glycyrrhizic acid as target analytes for detection. The content of glycyrrhizic acid is calculated by dividing the measured value of ammonium glycyrrhizinate by 1.0207. The chemical structures of these three compounds are shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.Chemical structures of three active components honokiol, magnolol, and glycyrrhizic acid in Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui herbal formula.
In the draft method, a C18 stationary phase is specified for the analysis of three compounds using two compound-specific methods, one for honokiol and magnolol, and another one for ammonium glycyrrhizinate. In the present study, honokiol and magnolol were analyzed using a superficially porous particle (SPP) Ascentis® Express C18 column to enhance separation efficiency, which allowed the use of a shorter column. Glycyrrhizic acid was determined with a fully porous particle (FPP) column offering extended pH stability (1.5-10.5), the Purospher® STAR RP-18e. The composition of a commercially available preparation of Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui was assessed using these two methods.
Experimental
Standard and Sample Preparation
Standards and samples were prepared according to the below procedures. The Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui was purchased from a local pharmacy.
Standard Preparation
For quantification of honokiol and magnolol:
- Mixed stock solution: Weigh 2.5 mg of honokiol and 5 mg of magnolol into a 10 mL brown glass volumetric flask. Add approximately 8 mL of methanol and sonicate for 5 minutes. Top up to the mark with methanol and mix well. The resulting concentrations of honokiol and magnolol in the stock solution are 250 μg/mL and 500 μg/mL, respectively.
- Standard solutions for external calibration: Pipette 2, 4, 10, 20, 40, 100, 200, 400, and 1000 μL, respectively, of mixed stock solution into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes. Dilute each to a final volume of 1 mL with methanol to obtain a series of standard solutions with concentrations of 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, and 250 µg/mL for honokiol and concentrations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500 µg/mL for magnolol.
For quantification of ammonium glycyrrhizinate:
- Stock solution (1 mg/mL): Weigh 10 mg of ammonium glycyrrhizinate into a 10 mL brown glass volumetric flask. Add approximately 8 mL of a 50% aqueous solution of ethanol and sonicate for 5 minutes. Top up to the mark with 50% aqueous solution of ethanol and mix well. The concentration of ammonium glycyrrhizinate in the resulting stock solution is 1 mg/mL.
- Standard solutions for external calibration: Pipette 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500 μL, respectively, of stock solution into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes. Dilute each to a final volume of 1 mL with 50% aqueous ethanol solution to obtain a series of standard solutions with concentrations of 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500 µg/mL of ammonium glycyrrhizinate.
Sample Preparation
Accurately transfer 5 mL of Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui into a 20 mL volumetric flask. Add 10 mL of ethanol, shake well, and dilute to volume with ethanol. Mix thoroughly and filter through a 0.45 μm membrane filter prior to HPLC analysis.
HPLC Methods
The quantification of honokiol and magnolol was performed using an Ascentis® Express 90 Å C18 column (Table 1), while ammonium glycyrrhizinate was analyzed on a Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped column (Table 2). Chromatographic conditions for each method are summarized in the respective tables.
Acceptance Criteria
The standard method requires that the theoretical plate numbers for magnolol and glycyrrhizic acid be NLT 5,000, and the resolution between the three analytes and their respective impurities must not be less than 1.5.
Results & Discussion
The chromatographic results of the HPLC analysis of honokiol, magnolol (Ascentis® Express C18 column), and ammonium glycyrrhizinate (Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped column) are shown in Figures 2 & 3 (standards) and Figures 5 & 6 (samples). Theoretical plate counts for all analytes exceeded 5,000, thereby fulfilling the requirements of the standard method (Tables 3 & 4).
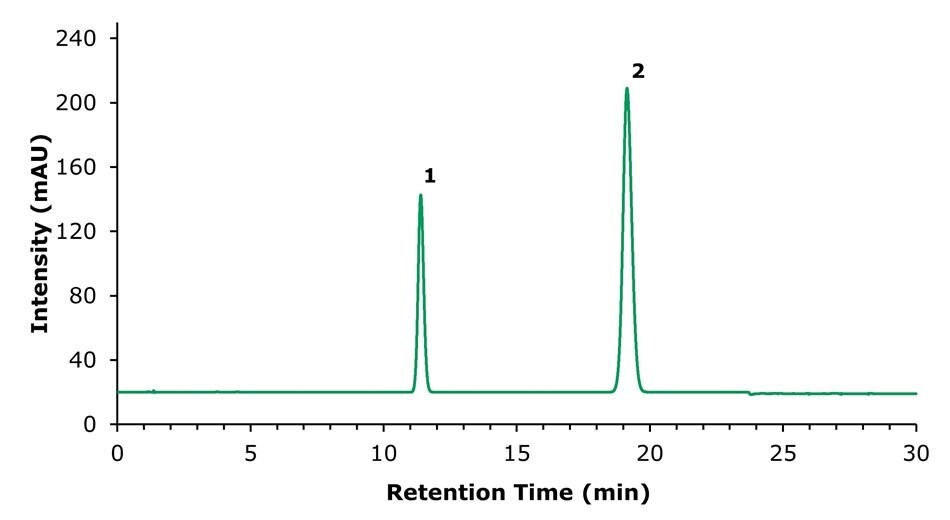
Figure 2.Chromatogram (294 nm) for the standard solution containing 100 µg/mL of honokiol (1) and 200 µg/mL of magnolol (2) obtained using the Ascentis® Express C18 column.
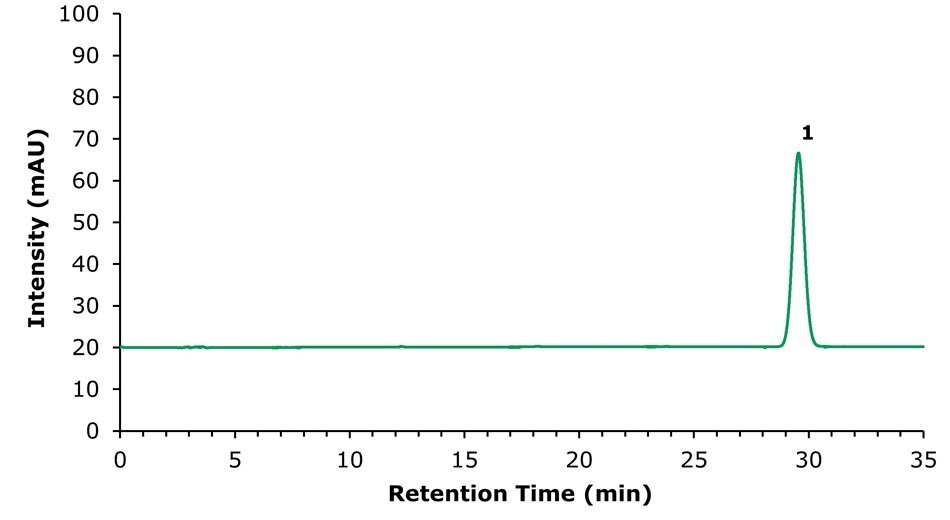
Figure 3.Chromatogram (253 nm) for the standard solution containing 200 µg/mL of ammonium glycyrrhizinate obtained using the Purospher® STAR RP-18 endcapped column.
Calibration, Sensitivity, and Repeatability
The calibration curve for honokiol is shown in Figure 4 as a representative example; similar results were obtained for magnolol and glycyrrhizic acid (calibration curves not shown). An overview of the calibration data for all compounds is provided in Table 5.
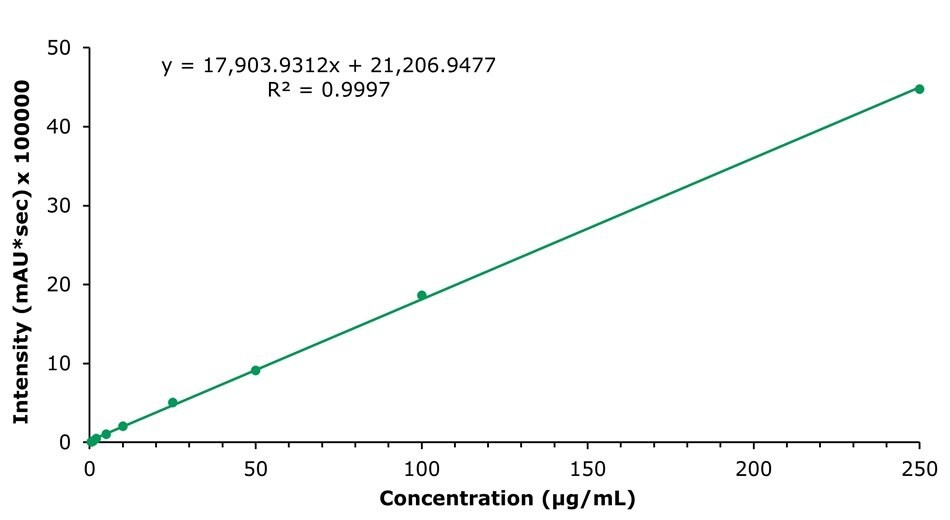
Figure 4.Calibration curve obtained for the analysis of nine honokiol standard solutions (c=0.5 – 250 µg/mL).
The LOD and LOQ for honokiol within the calibration range of 0.5 to 250 µg/mL were 2.13 and 6.46 μg/mL, respectively. For magnolol, the LOD and LOQ were 1.18 and 3.57 μg/mL within the range of 1 to 500 ng/mL. For glycyrrhizic acid, the LOD and LOQ were 0.40 μg/mL and 1.22 μg/mL within the range of 0.98–490 μg/mL (Table 6).
Repeatability was evaluated using five replicate injections of the standard solutions at concentrations of 100 µg/mL for honokiol and magnolol, and 200 μg/mL for ammonium glycyrrhizinate. The resulting relative standard deviation (RSD) values ranged from 0.13% to 0.64% (Table 7). These results comply with the general rule 0512 of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, which specifies that RSD values should be less than 2% unless otherwise stated, and provided RSD values between 0.13 and 0.64% (Table 7).
Sample Analysis
Real Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui samples were analysed, and the results are displayed in Figures 5 & 6 and Tables 8 & 9. In the method for ammonium glycyrrhizinate (Figure 6), an impurity peak was observed at 27.7 min. The resolution between ammonium glycyrrhizinate and the impurity was 2.3, thereby fulfilling the draft method requirement of >1.5. The determined content of honokiol, magnolol, and glycyrrhizic acid in the investigated Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui sample, obtained using the two developed methods, is summarized in Table 10.
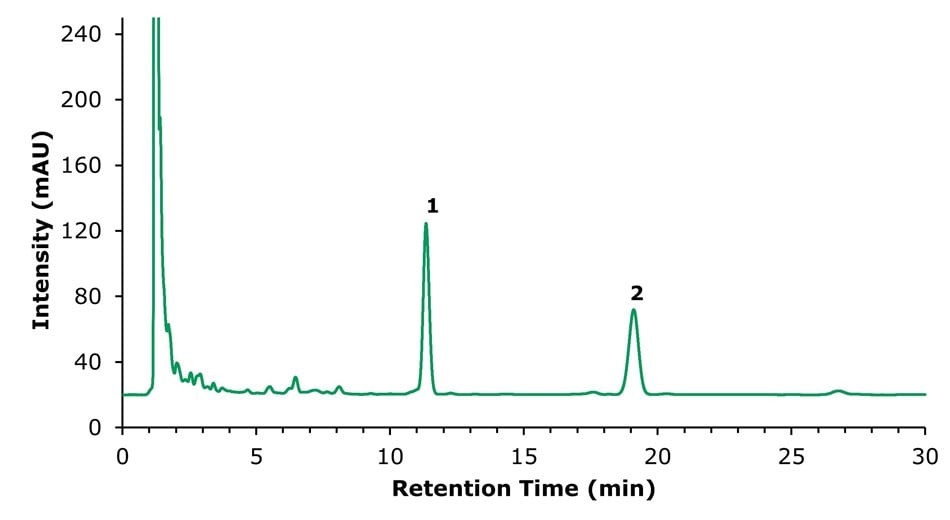
Figure 5.Chromatogram (294 nm) of the sample solution showing (1) honokiol, (2) magnolol.
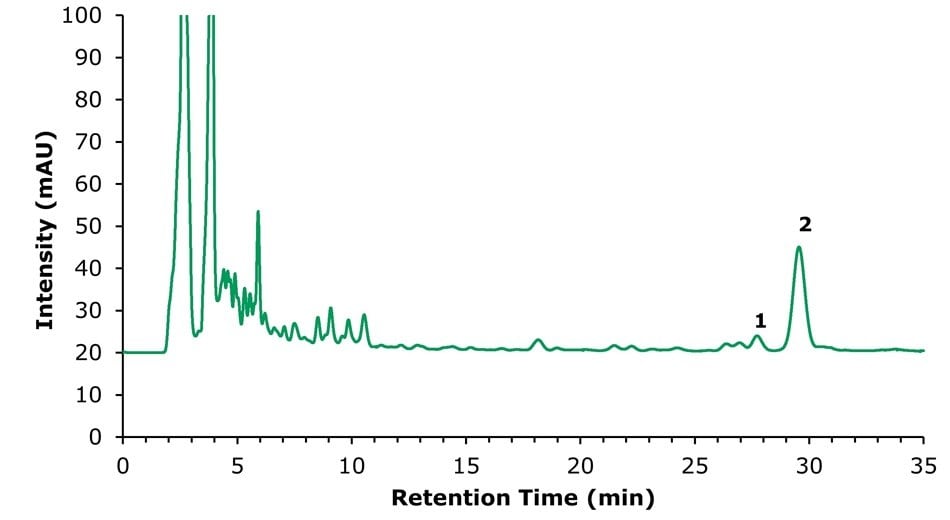
Figure 6.Chromatogram (253 nm) of the sample solution showing (1) unknown impurity, (2) ammonium glycyrrhizinate.
Conclusion
The analysis of the three active compounds, honokiol, magnolol, and glycyrrhizic acid, in a Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui formulation was demonstrated in accordance with the draft detection methods released by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Ch P) Commission. The sample was diluted with ethanol, filtered, and subsequently analyzed by HPLC-UV using an Ascentis® Express 90 Å C18 for honokiol and magnolol and a Purospher® STAR C18 endcapped column for glycyrrhizic acid. The developed methods fulfilled the acceptance criteria specified in the Ch P commission’s published draft regarding minimum theoretical plate count and resolution. These findings confirm the suitability and compliance of the two employed columns for the analysis of Huoxiang Zhengqi Shui in line with the pharmacopeial requirements.
Solvents, Reagents & Accessories
Reference Materials and Standards
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?