A Highly Sensitive IFN-γ ELISpot Assay to Quantify Cellular Immune Responses to Previous Viral Infection
Introduction
Developed in 1983, the ELISpot (Enzyme Linked Immuno-Spot) assay provides an effective method of measuring antibody or cytokine production of immune cells at the single-cell level.1,2 The popularity of this assay has seen a resurgence in recent years as researchers attempt to gain a better understanding of immune responses in a variety of applications including study of immunological memory and vaccine development.3
This study presents an example of a typical ELISpot assay for quantifying the number of pre-existing, antigen-reactive T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples obtained from donors previously infected with cytomegalovirus (CMV). As it is possible to obtain PBMCs based on the serostatus of CMV antibodies, T cell interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) immune response can be compared between CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative populations, where the former populations would have developed memory T cells specific to the virus. We show that donors with previous exposure to CMV exhibit significant presence of virus-specific T cells when compared to PBMCs from non-exposed donors based on IFN-γ secretion.
Since microporous membranes offer vastly improved binding characteristics over standard polystyrene surfaces, most ELISpot assays are currently performed on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane filter plates. Because the readout for an ELISpot is "spots per well", the PVDF membrane’s white color provides the ideal backdrop for spot detection and analysis. This filter plate format further offers greater throughput and is amenable to automation, enabling the processing of more samples under different experimental conditions within a single plate.
In the standard ELISpot assay (Figure 1), cytokine-specific antibodies are immobilized on 96-well membrane filter plates. Next, cells are seeded in the presence or absence of stimulating agents. Activated cells begin to secrete cytokines, which bind to the capture antibodies in the immediate vicinity of the expressing cell. Cells are then washed off and spot detection is accomplished through substrate deposition following either a one-step (enzyme-conjugated, cytokine-specific antibody) or two-step (biotinylated Ab/Streptavidin-enzyme) antibody binding process. Once the signals are developed, spot numbers can be tallied manually or by using image-based spot readers with accompanying analysis software.
We used MultiScreen® HTS-IP filter plates in an ELISpot assay to identify and enumerate CMV responsive, cytokine-secreting cells from isolated PBMCs. It has been shown that stimulation with CMV particles or CMV peptide pools can trigger inflammatory cytokine release in PBMCs obtained from CMV-seropositive donors in vitro.4,5 The ELISpot assay enabled enumeration of individual cells secreting IFN-γ in response to stimulation by CMV peptide. The assay was highly sensitive, permitting detection at the single cell level. This model has potential applications in antiviral vaccine development, allowing evaluation of vaccine efficacy by comparing cellular responses in clinical samples prior to and following vaccination.
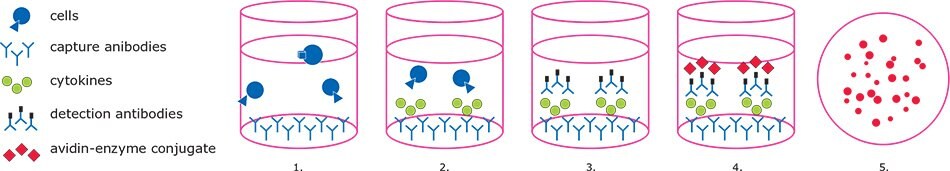
Day 1: Coating with capture Ab at 4 ºC overnight.
Day 2: Loading PBMCs and peptides and incubate cells at 37 ºC overnight.
Day 3: Develop spots by adding detection Ab and add avidin conjugates and substrates; Read and analyze data.
Figure 1. ELISpot workflow.
Materials and Methods
Reagents
- Single-donor peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) (CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative donors ages 20-30, AllCells)
- MultiScreen® HTS-IP filter plates (Merck, #MSIPS4510)
- Anti-human IFN-γ (MabTech, #3420-3-250)
- Anti-human IFN-γ, biotinylated (MabTech, #3420-6-250)
- Streptavidin-HRP (MabTech, #3310-9-1000)
- TMB substrate (MabTech, #3651-10)
- CMV peptide pool for human CD4 and CD8 T cells (Mabtech, #3619-1)
- RPMI 1640 + 10% FBS
- PMA (Merck, #5005820001)
- Ionomycin (Merck, #I3909)
- 35% ethanol
- Sterile water
- 1X PBS
Plate Preparation
- On Day 1, wells were pre-wet with 15 µL of 35% ethanol for less than 1 minute, then flicked to remove ethanol to avoid underdrain
- Wells were washed 4x with 200 µL sterile water
- 100 µL of capture antibody (10 µg/mL final concentration in 1X PBS) was added to each well and incubated overnight at 4 °C
Assay
- On Day 2, plates were washed 3x with 1X PBS (200 µL per well)
- Plates were conditioned with RPMI 1640 + 10%FBS medium (200 µL per well) for 30 minutes at room temperature
- Cells were seeded into wells and incubated overnight (16-20 hours) undisturbed in a tissue culture incubator (37 °C, 5% CO2):
- PBMCs from CMV-seropositive and CMV- seronegative donors: 100 µL of 50,000, 25,000, 12,500 cells per well in complete media containing CMV peptides (2 µg/mL final concentration)
- Positive control: 100 µL PBMCs activated with ionomycin (0.3 µM) and PMA (0.2 µM)
- Negative control (PBMCs from seropositive donors, in absence of CMV peptide stimulation): 100 µL of 50,000 cells per well in complete media
- On Day 3, cells were removed by aspirating the plates; wells were washed 4x with 1X PBS (200 µL per well)
- Plates were incubated for 2 hours at room temperature with biotinylated detection antibody (0.25 µg/mL in 1X PBS + 0.5% FBS, 100 µL per well)
- Plates were washed 5x with 1X PBS (200 µL per well)
- 100 µL of 1:1000 Streptavidin-HRP (in 1X PBS + 0.5% FBS) was added to each well and plates were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature
- Wells were washed 5x with 1X PBS (200 µL per well).
- TMB substrate (100 µL per well) was added and developed until spots appeared (~5 min)
- Color development was stopped by washing wells with ddH2O
- The underside of the membrane was rinsed with ddH2O before allowing membranes to dry
- Each well was examined using a Keyence™ VHX-2000 upright microscope. Images were digitally captured and used to count spots manually
Results
PBMCs from seven donors ranging from 20 to 30 years of age, composed of both CMV-seropositive (N=4) and CMV-seronegative (N=3) samples, were used for this study. As a positive control, PBMCs were activated with PMA-ionomycin to establish detection of IFN-γ responses (Figure 2). IFN-γ response was clearly observed, and the visual detection of high numbers of spots suggested significant stimulation of the seeded PBMC population by PMA-ionomycin. Though numerous, spots were evenly dispersed, reflecting uniform, high antibody coating of the MultiScreen® HTS-IP PVDF membrane surface. Titration of PBMC cell number resulted in a corresponding decrease in the number of spots visualized. Unstimulated PBMCs from CMV-seropositive donors were used as negative control. As expected, these samples did not produce any discernable IFN-γ cytokine response in the ELISpot assay (data not shown).
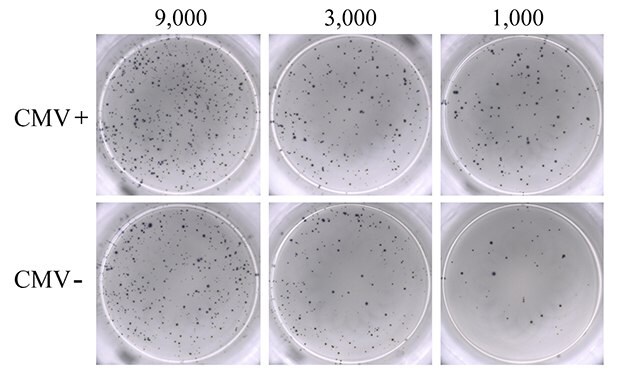
Figure 2.ELISpot assay using 0.3 µM ionomycin + 0.2 µM PMA to stimulate IFN-γ secretion from PBMCs. Results from CMV-seropositive (CMV+; upper panel) and CMV-seronegative (CMV-; lower panel) donors are shown. PBMCs were seeded into the MultiScreen® HTS-IP filter plate at three different densities as indicated (9,000, 3,000, and 1,000 cells/well). Untreated PBMCs from seropositive donors (negative control) showed results ranging from 0 to 3 spots (data not shown).
Next, PBMCs from CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative donors were compared for virus-specific IFN-γ response. A pool of peptides representative of the pp50, pp65, IE1, IE2, and envelope glycoprotein B proteins derived from human CMV was used to induce CMV-specific T cell responses. It is well-established that in vitro treatment of immune cells with antigenic CMV peptide pools stimulates production of IFN-γ and other cytokines.5 As expected, treatment of PBMCs from CMV-seropositive donors with the CMV peptide pool resulted in cellular secretion of IFN-γ (Figure 3). Spots were well-defined, suggesting uniform, high coating of the MultiScreen® HTS-IP PVDF membrane surface with antibody. In contrast, CMV-seronegative donor PBMCs stimulated with CMV peptide pools did not exhibit any detectable cellular IFN-γ secretion, indicating absence or extremely low frequency of CMV-specific T cells in PBMCs from non-exposed populations.
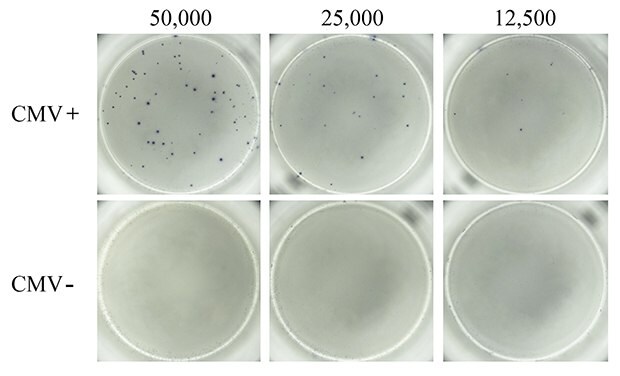
Figure 3.ELISpot assay using CMV-derived peptides to stimulate IFN-γ secretion. PBMCs from CMV-seropositive (top panel) and CMV-seronegative (bottom panel) donors were tested for the presence of CMV antigen-specific T cells capable of secreting IFN-γ upon CMV peptide stimulation. Samples from donors with a history of CMV infection (CMV+) produced numerous and well-defined spots corresponding to IFN-γ-secreting T cells when stimulated with the CMV peptide pool. Samples from donors who lacked previous infection (CMV-) failed to produce any detectable spots in response to the CMV peptide pool. Varying levels of cells were seeded into each well of a MultiScreen® HTS-IP filter plate as indicated.
Tabulated results are shown in Figure 4. Overall, the number of antigen-specific T cells secreting IFN-γ correlated with total number of seeded PBMCs from CMV-seropositive donor samples. For wells seeded with 50,000 PBMCs, a 60-fold difference in the number of spots was observed when comparing CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative samples (66 ± 13 spots vs. 1 ± 1 spots for CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative samples, respectively – Figure 4B).
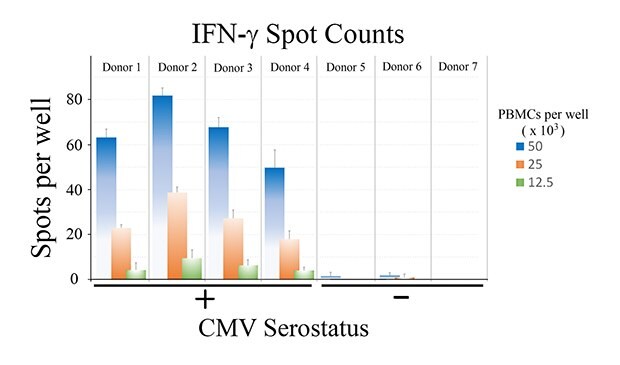
Figure 4a.
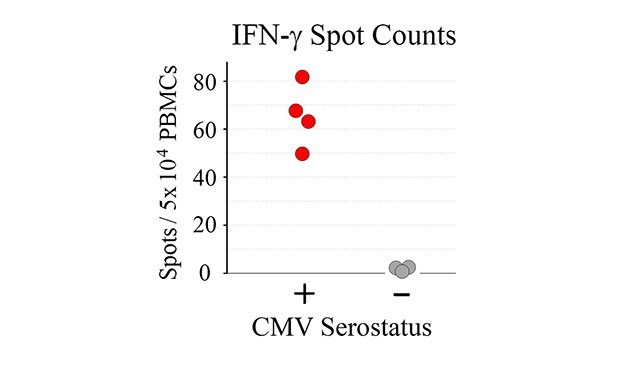
Figure 4b.
Figure 4. A) Quantitation of ELISpot results. B) Direct comparison of spot counts from wells seeded with 50,000 PBMCs. While donor-to-donor variability was observed, PBMCs from CMV-seropositive donors exhibited significant increases (p < 0.01) in the number of spots observed upon CMV peptide stimulation when compared to PBMCs from CMV-seronegative donors.
Conclusions
An ELISpot assay was used to evaluate cytokine production by PBMCs from CMV-seropositive and CMV-seronegative donors stimulated with a CMV peptide pool at the single-cell level. Significant differences in IFN-γ spot formation were observed between the two populations, where previous donor exposure to cytomegalovirus correlated to an increased number in CMV antigen-specific T cells. This ELISpot assay used a MultiScreen® HTS-IP filter plate with a PVDF membrane for cellular discrimination and visualization. Data showed uniform distributions of well-defined spots and a linear relationship of spots to seeded cell numbers, suggesting strong membrane binding properties, excellent optical properties, and a robust assay. The ELISpot assay was user-friendly and offers the potential for greater throughput by virtue of its automatable, microplate-based format.
Materials
References
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?