预设计siRNA
MISSION®预设计siRNA系与默克公司独家合作,采用独有的Rosetta Inpharmatics siRNA设计算法创建。Rosetta siRNA设计算法利用位点特异性打分矩阵和种子区域知识,预测目标基因最具效率和特异性的序列。该算法的规则基于超过三年的基因沉默实验实证数据开发。
产品优势
- 同类产品之中的佼佼者,基因沉默效果有保障
- 有效敲低低丰度信使
- 使用 11 阳性对照 siRNA 简化转染优化
- 使用 8 阴性对照 siRNA 区分序列特异性沉默和非特异性效应
- 数百种经过功能验证的预设计siRNA
产品特性
- 物种:人类、小鼠和大鼠
- 规格:2 (10 nmol)、5 (25 nmol)和10 (50 nmol) OD
- 纯化方法:脱盐或HPLC
- 序列形式:具有 dTdT 突出端的 21mer 双链体
- 质检方法:100%质谱分析*
- 形式:以管装干粉形式提供
*部分生产基地可能采用PAGE方法评估siRNA双链体。
预设计产品保证
以 ≥30 nM 的浓度转染时,在三份靶向同一基因的 MISSION® 预设计siRNA中,至少两份可将培养细胞中的靶标 mRNA 水平降低 75%。如果其中两份siRNA未能将目标基因敲低 75%,我们将免费再提供三份该基因的 siRNA。如果无法继续提供该基因的siRNA或所有siRNA均未能将目标基因敲低 75%,我们将原价退款。
上述保证需提供有关转染效率的适当支持数据。转染效率的适当支持数据包括 qPCR 数据,将转染≥30 nM 的 MISSION 阳性对照 siRNA(GAPDH、MAPK1、TP53 等)的靶标 mRNA 水平与适当的阴性对照(例如模拟转染、加扰siRNA 序列或 MISSION 通用阴性对照 siRNA)进行对比,证明靶标 RNA 的敲低率小于 75%。
由于抗体和蛋白质半衰期不定,我们不接受基于蛋白质的检测方法数据。
产品库
一种流行的混合形式是 4 种 5 nmol 双链,混合到一支管中(20 nmol 混合);另一种形式也是 4 种 5 nmol 双链,但每种单管装(20 nmol 单装)。即便如此,我们先进的液体处理器还允许更多组合。如需针对您特定的需求进行可行性评定,请电邮sirnarequest@sial.com。
经验证的siRNA
许多常见基因靶标已经过 ≥75% mRNA 敲低验证(图 1提供了数据示例以及常订购的经验证siRNA清单表(按基因符号)。经验证的siRNA适于转染优化或用作阳性对照。
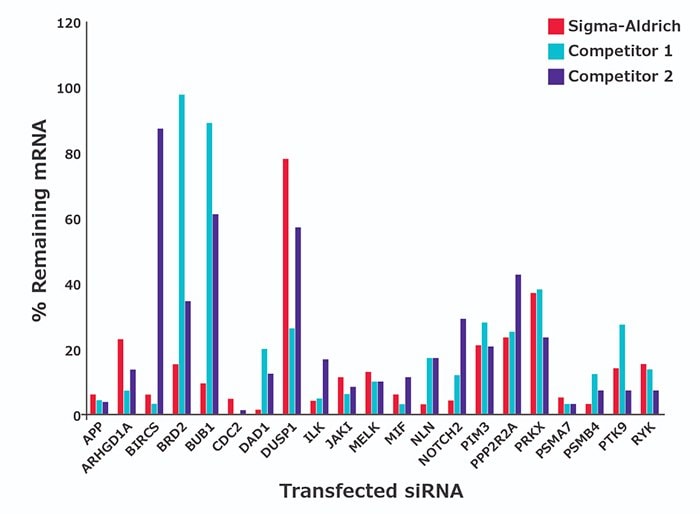
图 1.用30 nM 浓度的预设计siRNA 转染 HeLa 细胞。转染后 48 小时,通过 qPCR 测定剩余基因表达水平的百分比(相对于模拟物)。数据为四份生物学重复的均值。
材料
精选引用文献
如果需要其他帮助,请通过oligotechserv@sial.com咨询我们的技术服务组。
MISSION是德国默克(Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany)及/或其附属公司的商标。标签许可证。
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?