Determination of Choline in Infant Milk Powder Acc. to GB Method 5413.20-2022
Abstract
High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used to analyze choline in infant dairy products. The results show that the method is fast and meets the performance criteria of the GB 5413.20-2022 "Determination of choline in infant and young children’s foods and dairy products.” It also offers greater efficiency compared to HPLC-UV/DAD methods.
Section Overview
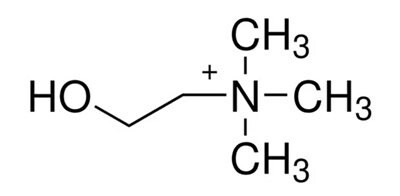
Figure 1.Choline structure
Choline (Figure 1) is a quaternary ammonium cation distributed in organisms in the form of free choline, acetylcholine, and phospholipid complexes. It is involved in the formation of biofilm proteins and is also closely related to the movement of the central nervous system, making it a critical substance in human metabolism. To ensure choline intake, a certain amount of choline is usually added in the form of tartrate or chloride in formula milk powder, health products, and infant complementary foods.1
In the new infant formula food standards GB 10765-2021 "Infant Formula Food" and GB 10766 "Larger Infant Formula Food" released in 2021, choline was upgraded from an optional ingredient to an essential ingredient. The specified test method is also updated to GB 5413.20-2022 "Determination of choline in infant food and dairy products". This new standard was implemented on February 10, 2023.1-3
For a choline determination in food matrix, interferences can be severe, and an HPLC-UV method can be challenging to meet the required sensitivity. Therefore, we used liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry to analyze the choline content in infant milk powder. More specifically, an LC-MS/MS approach was employed, which allowed for simple operation, high sensitivity, and excellent reproducibility. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode and isotope-labelled internal standard addition were combined to quantify the content of choline in the samples (reported as choline hydroxide equivalent in accordance with GB method). The developed method here is compared to the requirements stated in the GB 5413.20-2022.4
Experimental
The analysis was performed in accordance with the draft GB method using the following procedures:
Reagent Preparation
- Ammonium formate solution (10 mmol/L): Weigh 0.63 g ammonium formate, dissolve in water, and adjust pH to 5.0 ± 0.1 by adding formic acid. Transfer the solution to a 1 L volumetric bottle, adjust the volume with water to the mark, and mix.
- Hydrochloric acid solution (1 mol/L): Measure 8.5 mL concentrated hydrochloric acid, transfer it to a 100 mL volumetric bottle, fill with water to the mark, and mix well.
- Sodium hydroxide solution (1 mol/L): Weigh 2.0 g sodium hydroxide, dissolve in water, and dilute to 50 mL.
- Acetonitrile solution (80%): Measure 80 mL acetonitrile and fill up to 100 mL with water.
Standard Preparation
- Choline standard solution I (100 mg/L as choline hydroxide): Weigh 11.52 mg of choline chloride standard, which has a MW of 139.62 g/mol equivalent to 10.00 mg choline hydroxide (MW 121.18 g/mol) which is used as base for reporting, and dissolve in 80% acetonitrile solution to obtain a final volume of 100 mL. After shaking, transfer the solution to an amber glass bottle and store at 4 °C and protected from light.
- Choline standard solution II (1.0 mg/L as choline hydroxide): Pipette 1.0 mL of choline standard solution I into a 100 mL amber glass volumetric flask and fill to the mark with 10 mmol/L ammonium formate solution to obtain a 1.0 mg/L choline standard solution II. Store at 4 °C and protected from light.
- Choline-D4 standard solution I (1000 mg/L): Weigh 13.3 mg of choline-d4 chloride standard, which is with MW of 143.65 g/mol equivalent to 10.00 mg choline-D4 (MW 108.01 g/mol), dissolve in 80% acetonitrile solution, transfer to a 10 mL amber glass volumetric bottle, fill to the mark with 80% acetonitrile solution, and mix well. Store at 4 °C and protected from light.
- Choline-D4 standard solution II (1.0 mg/L): Pipette 0.1 mL of choline-D4 standard solution I into a 100 mL amber glass volumetric flask and fill to the mark with 10 mmol/L ammonium formate solution to obtain a 1.00 mg/L choline-D4 standard solution II. Store at 4°C, protected from light.
- Choline standard working solutions 1-7: Prepare a total of seven standard working solutions (nos. 1-7, as required by the GB method) by pipetting 0.01 mL, 0.10 mL, 0.20 mL, 0.50 mL, 1.0 mL, 1.5 mL, and 2.0 mL of choline standard solution II into six separate 10 mL volumetric flasks. Add 500 μL of choline-D4 standard solution II to each of the flasks. Fill to the mark with 10 mmol/L ammonium formate and mix well. The concentrations of choline (as choline hydroxide) in the standard series are 1.00 µg/L, 10.0 µg/L, 20.0 µg/L, 50.0 µg/L,100 µg/L, 150 µg/L, and 200 µg/L, respectively as choline hydroxide equivalent. The solutions are intended for immediate use.
Sample preparation
- Extraction: Weigh 1 g of milk powder and put it into a 100 mL beaker. Add 80-85 mL of pure water at 75 °C, mix well until it is completely dissolved, then cool it to 25 °C for use in the cleanup step.
- Cleanup: Add 10 mL of 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution and 50 μL of choline-D4 internal standard solution I to the sample extract above, mix thoroughly, and ultrasonicate for 5 minutes. Heat the sample solution in a water bath at 70 °C ±2 °C for three hours (shake the solution every 30 min). Allow to cool down to room temperature and adjust to pH 5.0-5.3 with 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution. Transfer the solution to a 100 mL volumetric bottle, dilute to the mark with 10 mmol/L aqueous ammonium formate solution, and mix well. Filter through a 0.22 μm Millex® Syringe Filter, PES into a sample bottle.
- Spiking experiments: Prepare two samples for the determination of recovery (%) and precision by spiking 1.0 g each of blank milk powder sample with 100 μL and 200 μL choline standard solution II, respectively. The concentration of choline in the two resulting infant formula samples is 100 µg/kg and 200 µg/kg as choline hydroxide. Subsequent sample preparation is performed as described above. Use the infant milk powder sample with a choline concentration of 200 µg/kg for the determination of analysis precision and the infant milk powder sample with a choline concentration of 100.0 µg/kg for the analysis of recovery rate (%).
LC-MS/MS analysis
The standard solutions and resulting extracts were analyzed by HPLC using a Fused-Core® Ascentis® Express RP-Amide column and MS/MS detection (Table 1).
Results and Discussion
Infant milk powder samples were dissolved in warm water, adjusted to pH 5.0-5.3 with 1 mol/L sodium hydroxide solution, and filtered. The samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and quantified by the isotope internal standard method.
Standard chromatogram
The results for the LC-MS/MS analysis of the choline standard solution (10.0 μg/L as choline hydroxide equivalent) are shown in Figure 2. Table 2 displays the chromatographic data for Figure 2.
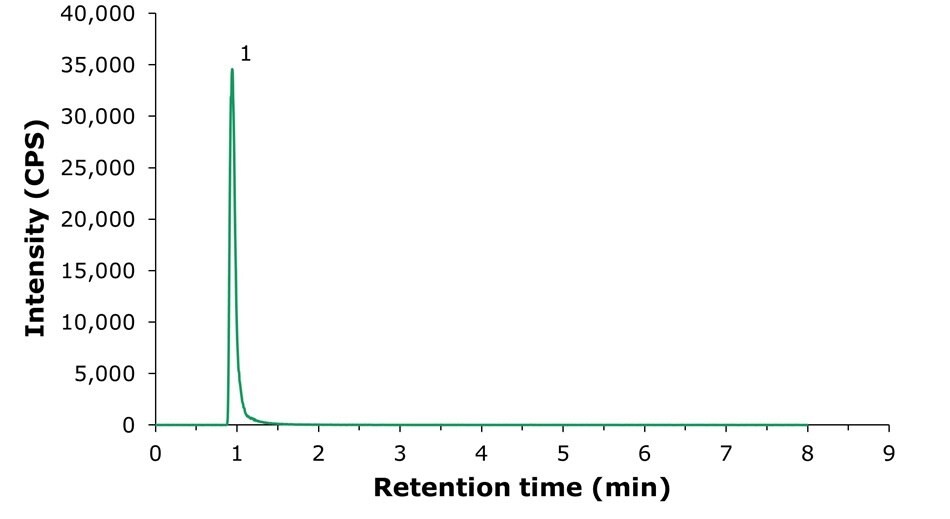
Figure 2.LC-MS/MS chromatogram displaying the analysis of choline standard working solution (10 μg/L as choline hydroxide equivalent). 1: choline (tr = 1.03 min). MRM transitions: 104.096 -> 45.153 (quantitative).
Calibration
The results for the external calibration experiments in the range of 1.0-200 µg/L (as choline hydroxide equivalent) are shown in Figure 3 and Table 3. The linearity of the calibration showed an R2 value of 0.9995, meeting the GB 5413.20-2022 criteria of ≥ 0.9980.
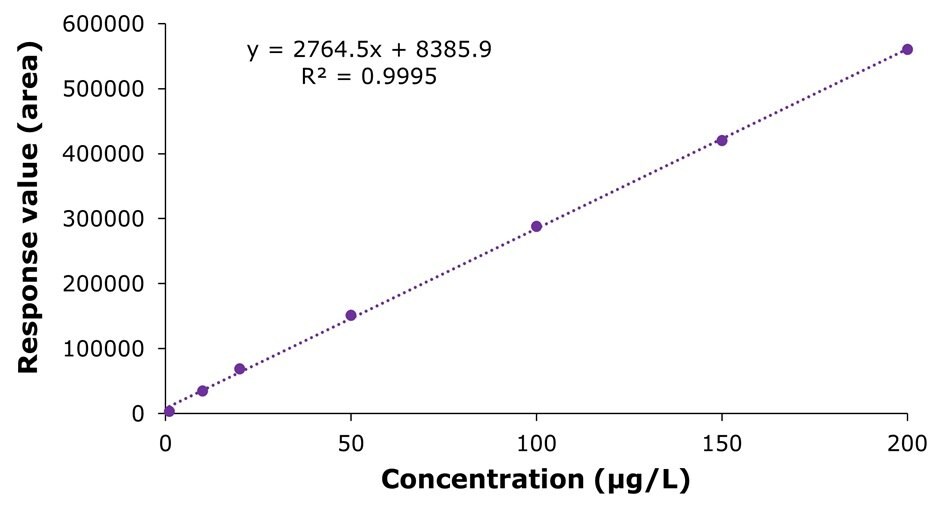
Figure 3.Calibration curve obtained by the analysis of standard solutions 1-7 (1.00, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0, 100, 150, and 200 μg/L as choline hydroxide equivalent).
Data Precision and Recovery (%)
The infant formula samples used were shown to be free of choline. The sample spiked with choline at 200 µg/kg (as choline hydroxide equivalent) was used for precision evaluation (Figure 4). The results are shown in Table 4. The RSD at the test concentration was 1.13% (GB 5413.20-2022 specifies an RSD limit of ≤ 20%).
The results of the recovery determination experiment using the second spiked sample at a spiking level of 100 µg/kg (as choline hydroxide equivalent) in infant formula milk powder are shown in Table 5. The % recovery was 86.0 to 89.0% (GB 5413.20-2022 specifies a required recovery of 70 - 120%).
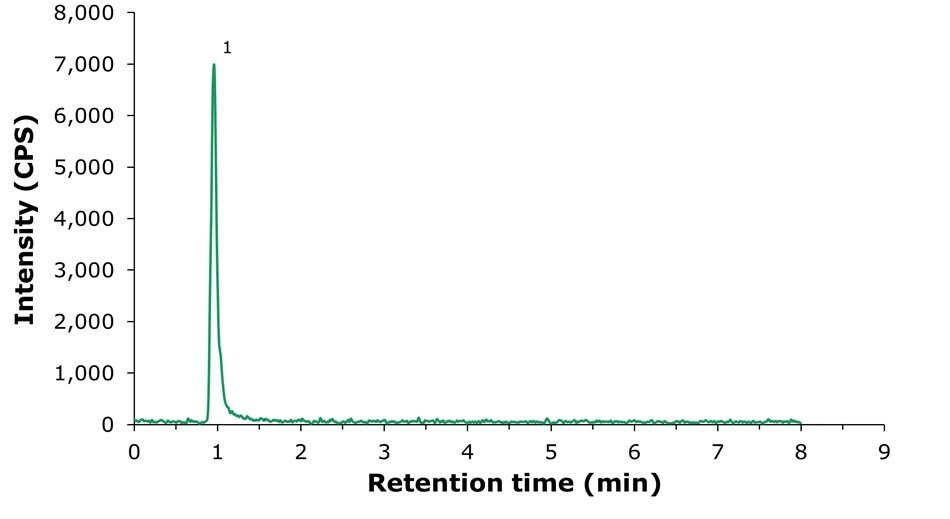
Figure 4.LC-MS/MS chromatogram obtained by the analysis of an infant milk powder sample utilized for the determination of method precision. The sample was spiked with choline at a concentration of 200 µg/kg (as choline hydroxide equivalent). 1: Choline (tr = 1.03 min). MRM transitions: 104.096 -> 45.153 (quantitative).
Sensitivity
Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ) were calculated according to the GB method using baseline noise of a blank sample: LOD (3N/X); LOQ (10N/X). The LC method’s sensitivity was determined with a limit of detection (LOD) of 2.00 µg/kg, and a limit of quantification (LOQ) of 6.00 µg/kg (Table 6) and by that exceeding the GB methods requirements.
Real Sample Measurement
In Figure 5, the result for the analysis of an unspiked infant milk powder sample is shown. No choline peak is visible in this chromatogram.
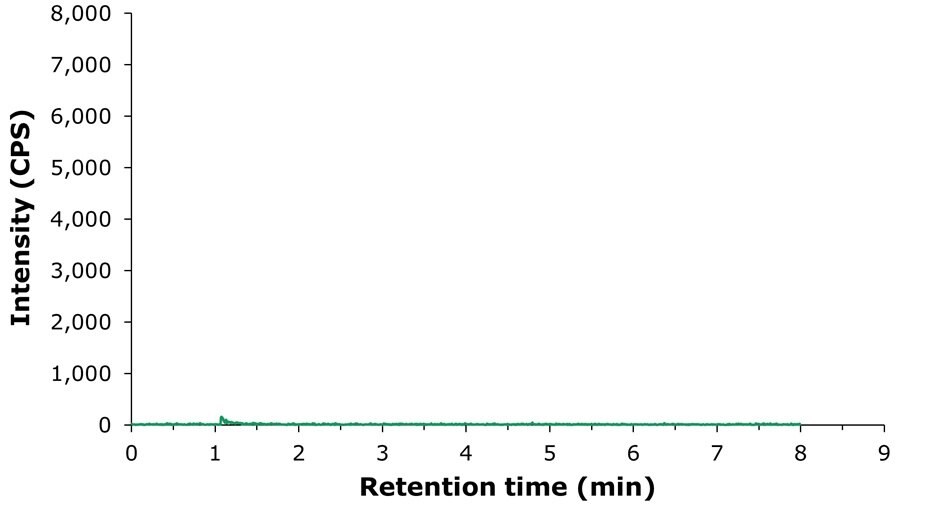
Figure 5.LC-MS/MS chromatogram obtained by the analysis of an unspiked infant milk powder sample. MRM transition: 104.096 -> 45.153 (quantitative).
Conclusion
A high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method for quantifying choline in infant formula milk powder was established. Samples were dissolved in warm water and hydrolyzed with acid to adjust the pH. The supernatant was filtered and analyzed using an RP-Amide U/HPLC column. Detection was performed by applying an MRM mode. Quantification was performed using an external calibration and isotope-labeled internal standard addition approach. The method showed excellent linearity for choline in the concentration range from 1 to 200 µg/L (as choline hydroxide equivalent), with correlation coefficients greater than 0.9980. The limit of detection (LOD) for choline was 2.00 µg/kg and LOQ 6.00 µg/kg. The average recoveries were 87.4% and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n=7) was 1.13%. It was demonstrated that the developed method enables straightforward sample preparation, high sensitivity, and accurate quantification, making it suitable for rapid detection of choline in infant formula milk powder and meeting the GB methods criteria.
Related Products
HPLC Column
Sample Preparation, Solvents, Reagents, & Consumables
Reference Materials
References
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?