GlycoProfile™ ß-Elimination Kit
Expect More!
The first and only way to simultaneously separate O-glycans from protein.
Now you can have your O-linked glycans and protein too!
Our GlycoProfile™ ß-Elimination Kit allows researchers to:
- Perform complete glycoproteomics research by preserving both the O-glycans and protein
- Specifically remove O-glycans
- Label O-glycans prior to analysis
- Have confidence in uniformity of procedure

Enabling Proteomic Analysis | O-glycan Analysis | Ordering Information
While it is known that O-glycosylation plays a major role in regulatory biology (as evident with studies around O-GlcNac and RNAi knockdowns of glycosyltransferases) the development of methods for the study of O-glycosylation is under represented compared to N-glycosylation. The under representation is primarily due to the difficulty in removing O-glycans while keeping both the protein and glycans intact. In contrast to N-glycosylation, there is no single enzyme capable of complete O-deglycosylation, so chemical methods must be employed.
Traditionally, alkaline β-elimination uses a combination of sodium hydroxide and sodium borohydride. The O-glycan linkage is easily hydrolyzed using dilute alkaline solution under mild conditions. The presence of a reducing agent can keep the glycan from "peeling" after being released, but the process significantly degrades the protein or peptide. Other methods, such as using sodium hydroxide alone or with borane-ammonia, also easily hydrolyze the linkage, but are not very efficient at keeping both moieties intact.
A novel non-reductive β-elimination kit has been developed that keeps both protein and glycan intact. The method is much easier to use than the traditional β-elimination methodologies. There is no tedious neutralization of the borohydride or ion exchange chromatography to be performed. This technology allows for complete glycoproteomic analysis of O-linked glycoproteins, as never before possible.
Enabling Proteomic Analysis
Our GlycoProfile™ ß-Elimination Kit allows for proteomic analysis, in that it does not completely destroy the protein, as seen with other traditional methods of β-elimination.
This is illustrated by SDS-PAGE of proteins before and after deglycosylation. Gel has been stained with EZBlue™ (G1041) and destained with water.
 |
Lane 1: ColorBurst™ Marker, High Range (C1992) Lanes 2 and 3: Fetuin prior to β-elimination Lanes 4 and 5: Fetuin incubated in 50 mM NaOH overnight Lanes 6 and 7: Fetuin incubated in NaBH4 and NaOH overnight (traditional β-elimination) Lanes 8 and 9: Fetuin incubated in our β-elimination reagent at 4-8 °C overnight Lanes 10 and 11: Fetuin incubated in our β-elimination reagent at room temperature overnight Lane 12: SigmaMarker™, wide range (S8445) |
There is no need to sacrifice sample to divide between glycan and protein analysis. Proteomic analysis by LC-MS prior to deglycosylation gives equivalent sequence coverage.
Trypzean™, before deglycosylation

Trypzean™, after deglycosylation

Glycophorin A, before deglycosylation

Glycophorin A, after deglycosylation

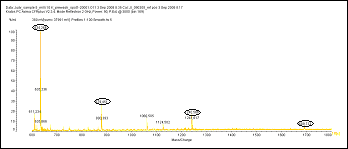
A.Fetuin
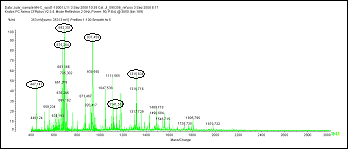
B.Mucin
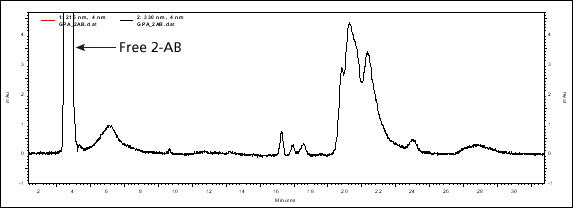
Since the β-elimination reagent is non-reducing, labelling of the O-glycans, such as with 2-AB, is possible. This is illustrated below with the chromatogram of O-glycans from Glycophorin A following 2-AB labelling.
Materials
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?