Palladium-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions
A variety of widely used palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions can be run under mild room temperature conditions in water with TPGS- 750-M, using a variety of commercially available palladium complexes and ligands. These transformations, including Suzuki-Miyaura, Sonogashira, Buchwald-Hartwig aminations, and Heck, are amongst the most heavily used bond-forming reactions, both industrially and academically (Scheme 1).
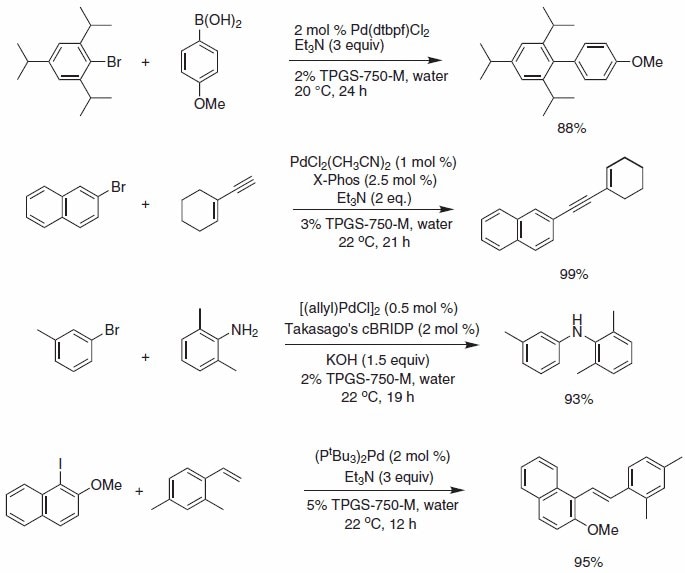
Scheme 1.Selected Pd-catalyzed cross coupling reactions.
Operationally, simple Suzuki-Miyaura reactions using micellar catalysis and bis(di-tert-butylphosphino)ferrocene palladium chloride complex provide access to highly sterically congested substrates at room temperature using triethylamine as base.
Sonogashira reactions and Buchwald-Hartwig aminations are also amenable to reaction in water with TPGS-750-M using the palladium chloride/X-Phos combination in the former, and allyl palladium chloride/ cBRIDP in the latter (Figure 1).
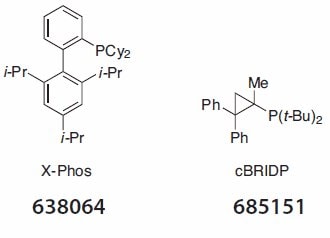
Figure 1.Selected ligand example (Product No. 638064).
Heck cross-couplings with aryl iodides can be successfully performed using Pd(P(t-Bu)3)2 as the palladium source in the bulk aqueous environment containing TPGS-750-M (5 wt. %), obviating the need for high temperatures commonly associated with Heck reactions.
Zinc-mediated Negishi-like couplings between aryl and alkyl halides can be performed in aqueous TPGS-750-M (Scheme 2). Under these conditions, typically highly moisture-sensitive organozinc halides are formed in situ from an alkyl halide and zinc dust, and react with an aryl halide under palladium catalysis. With the aid of a surfactant and a stabilizing ligand for RZnX, such as tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA), this entire process takes place in water, leading to a variety of primary and secondary alkyl-substituted aromatics. The choice of catalyst is crucial for the success of the reaction; Pd(Amphos)2Cl2 (Bis(di-tert-butyl (4-dimethylaminophenyl)phosphine) palladium(II) chloride) was found to be the optimal catalyst.
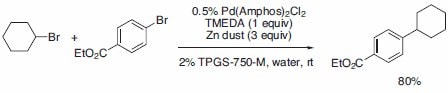
Scheme 2:Selected Negishi-like cross-coupling example.
Materials
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?