Auto2D® 2-D Gel Electrophoresis Device Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between the isoelectric focusing (IEF) chip pH3-10 and pH3-10NL?
- What is the difference between the Auto2D® mode and Auto2D® Plus mode?
- How is the IEF chip selected?
- How is the Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) chip selected?
- Which ampholyte should I use?
- How much is the appropriate sample amount?
- What labeling dye can be used for the Auto2D® device?
- How do the detergents in the sample affect two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE)?
- What do you recommend for purification or desalting of samples?
- How do I prepare the sample using immunoprecipitation (IP)?
- How do I interpret the graphs for voltage and current?
- Is it possible to perform alkylation of cysteine during automatic operation?
- Can I perform the 2DE in a non-reducing environment?
- Can I perform the 2DE in the native environment?
For additional resources on gel electrophoresis equipment and reagents, please visit our Electrophoresis Systems & Transfer Equipment resource hub.
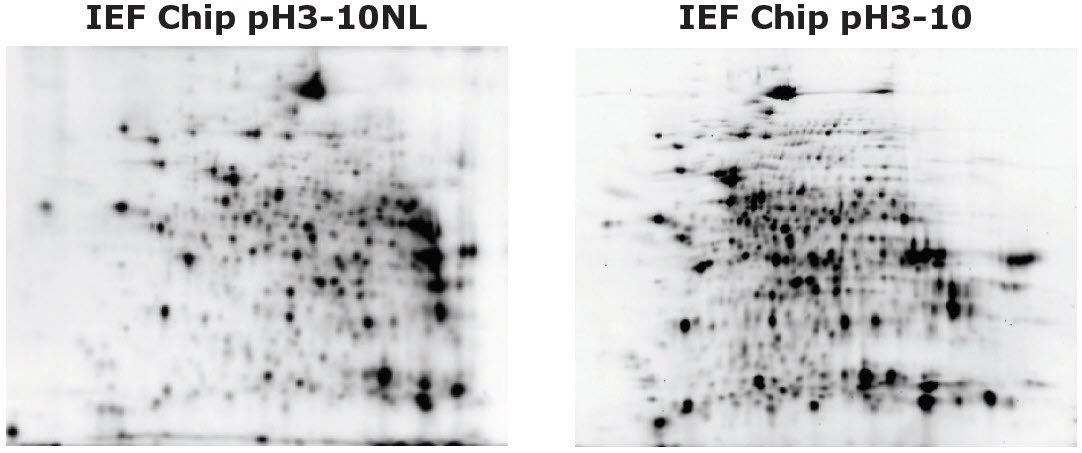
Auto2D® Device IEF Chip pH3-10 and IEF Chip pH3-10NL
2. What is the difference between the Auto2D® mode and Auto2D® Plus mode?
Auto2D® Plus mode is the improved operation mode. It actively loads proteins into a wet gel by applying voltage. Compared with Auto2D® mode, which adopted a conventional electrophoresis method, the sample loading efficiency is very high with a 30-minute shorter run time. Because larger protein amounts can be applied and the protein absorption rate into the gel is higher with Auto2D® Plus mode, you can detect more spots compared to the Auto2D® mode. In the Auto2D® Plus mode, there are some new features to simplify sample preparation, including Desalt recipes and Auto-Stain recipes. Auto2D® Plus mode is highly recommended unless you need to keep consistency with previous data obtained by the Auto2D® mode
3. How is the IEF chip selected?
If you would like to analyze proteins comprehensively, select the IEF chip pH3-10 or pH3-10NL. If you would like to have better resolution in narrower pH range, select the IEF chip pH4-7 or pH6-10. If you want to analyze specific proteins, select the IEF chip pH4-5.5, pH5-6.5 or pH7-10.
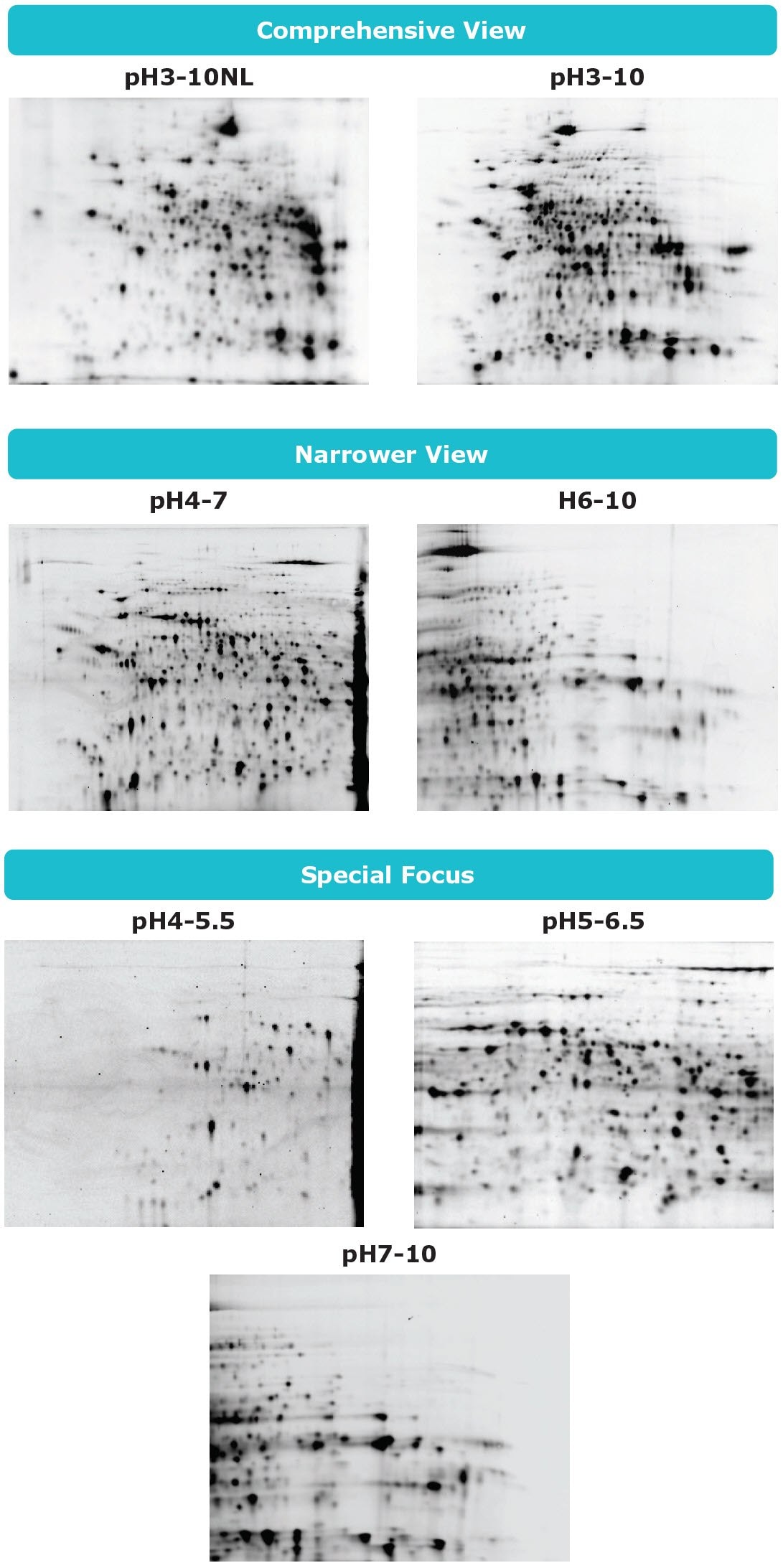
Auto2D® IEF Chip Selection
4. How is the Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) chip selected?
The separation range (kDa) of each PAGE chip (6.5%, 7.5%, 10%, and 12.5%) is shown in the figures below.
- 10%: Balanced distribution
- 12.5%: Balanced distribution with more focus on the lower molecular weight range
- 7.5%: Focus on higher molecular weight range
- 6.5%: Further focus on higher molecular weight range over 100kDa
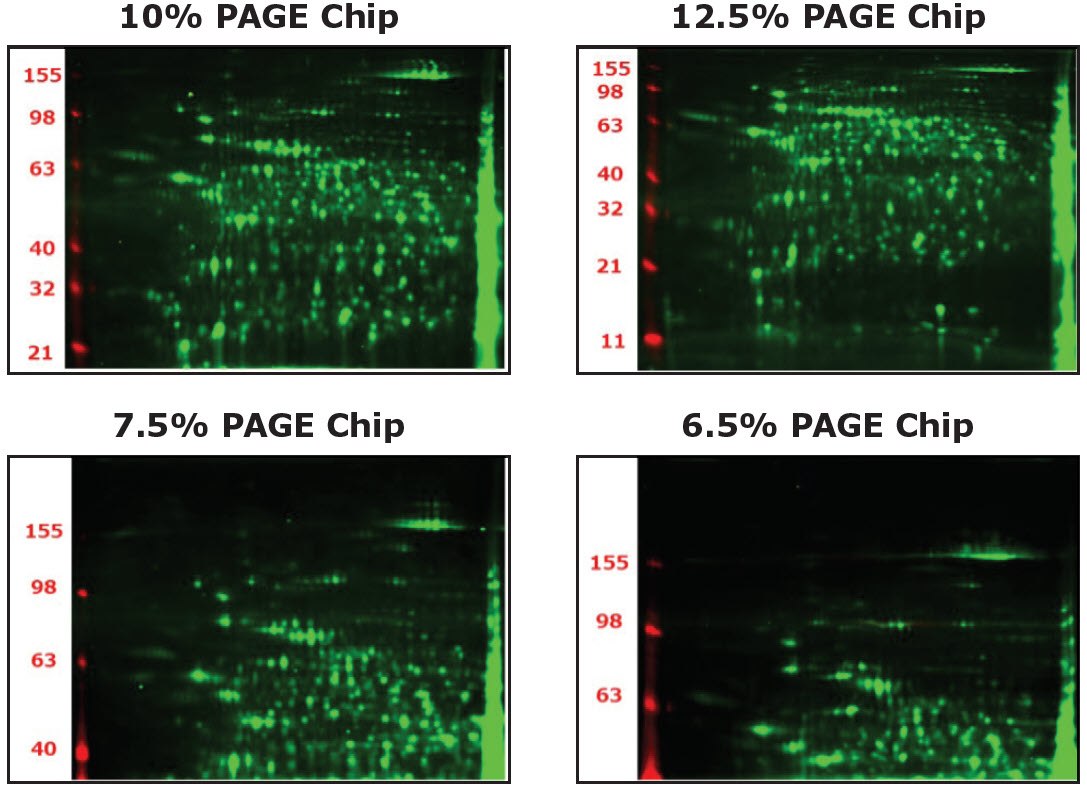
Auto2D® IEF PAGE Chip Selection
5. Which ampholyte should I use?
We recommend the following ampholytes.
For the IEF chip pH3-10NL:
- IPG buffer pH3-10NL (17-6000-88, Cytiva)
For the IEF chip pH3-10:
- BioLyte® 3/10 100X (1632094, Bio-Rad) *Add 2 µL of BioLyte® to Rehydration solution.
- Mixture of ZOOM™ Carrier Ampholytes pH3-10 (ZM0021, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Pharmalyte® 3-10 (17-0456-01, Cytiva / P1522, Sigma-Aldrich), Ratio 1:1
For the IEF chip pH4-7, pH4-5.5, and pH5-6.5:
- IPG buffer pH4-7 (17-6000-86, Cytiva)
- Carrier Ampholytes pH4-7 (ZM0022, Thermo Fisher Scientific)
For the IEF chip pH6-10 and pH7-10:
- IPG buffer pH6-11 (17-6001-78, Cytiva)
6. How much is the appropriate sample amount?
The sample amount depends on the detection method. The recommended sample amounts are as follows.
- CBB staining: 25 µg or more
- Fluorescent staining: 25 µg or less
- Silver Staining: 10 µg or less
- Fluorescent pre-labeling: 3 µg or less
7. What labeling dye can be used for the Auto2D® device?
Samples can be pre-labeled using fluorescence dye reagent prior to electrophoresis. In 2-D electrophoresis, it is necessary to use dyes that do not affect the isoelectric point (total charge) of the proteins. Proven methods include the following.
- Labeling of the primary amine (N-terminal, Lys) using reagents with NHS-ester
- e.g.: Cy2/Cy3/Cy5 minimal labeling dye (Cytiva), IC3/5-OSu special packaging (Dojindo) or Cyanine 3/5 NHS ester (Abcam)
- Labeling of the sulfhydryl group (-SH, S-S) using reagents with maleimide
- e.g.: Cy2/Cy3/Cy5 saturation labeling dye (Cytiva)
8. How do the detergents in the sample affect two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DE)?
It depends on the type of the detergent and the concentration. Ionic detergents with strong polarity cannot be used. For example, if the sample contains SDS, dilute it appropriately or remove it using a 2-D Clean-Up Kit. In some cases, the nonionic (uncharged) detergents such as DDM can be used. If possible, use CHAPS, which is the same as included in Rehydration Solution.
9. What do you recommend for purification or desalting of samples?
We often use the 2D Clean Up Kit and Zeba™ desalt spin columns for sample preparation. We recommend the 2D Clean-Up kit for low-concentration samples to ensure maximal sample retention. The Zeba™ desalt spin column is faster than the 2D Clean Up kit and we recommend it for samples of sufficient concentration as there is slight sample loss during concentration.
10. How do I prepare the sample using immunoprecipitation (IP)?
We recommend the following for sample preparation using IP.
- If you don't reuse the antibody for IP, we recommend eluting the sample with the Rehydration Solution. You can apply the sample to the Auto2D® device without buffer exchange.
- If you elute the sample with another buffer, exchange the buffer to the Rehydration Solution with the 2D Clean Up kit and Zeba™ desalt spin column before applying it to the Auto2D® device.
11. How do I interpret the graphs for voltage and current?
You can utilize each graph as indicators of a successful 2DE and as to improve sample preparation. The current peak at 200V comes from the charged small molecules such as salts. The current peaks at about 1000V comes from charged medium-sized molecules, such as lipids and peptides. The current peak at the high-voltage step comes from the charged larger-sized molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. If the current at the final step of the IEF process is stable below 50 µA, the successful separation is likely to occur. In the IEF, the current value gradually decreases and settles as the sample proteins have been focused on their Individual isoelectric points.

Auto2D® Device Voltage and Current Graphs
12. Is it possible to perform alkylation of cysteine during automatic operation?
Yes, alkylation of cysteine during automatic operation is possible. Apply 700 µL of Equilibration Buffer containing 2-3% iodoacetamide to the vacant Equilibration groove 2 of the solution chip. And edit the recipe as follows.
- Touch the buttons in the order of "SETTING" → "RECIPE" to move to the maintenance mode.
- Load the recipe to edit.
- Touch the "SDS Equilibration 2" checkbox on the "SDS Equil." tab to activate it and set the time to 5 minutes.
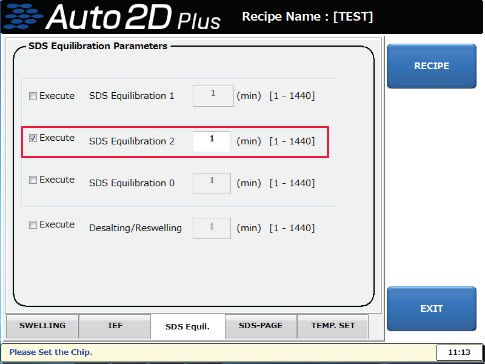
Auto2D® Device Alkylation of Cysteine
4. Save it as a new recipe.
13. Can I perform the 2DE in a non-reducing environment?
You can perform the 2DE in the non-reducing environment by preparing the Working Rehydration Solution and or the Equilibration Buffer without DTT. If you perform the 2nd dimension in the non-reducing environment, we recommend using Equilibration Buffer with urea.
Equilibration Buffer with Urea: 7.5M Urea, 20w/v% Glycerol, 125 mM Tris HCl pH6.8, 5w/v% SDS, 0.01w/v% BPB
14. Can I perform the 2DE in the native environment?
You can perform the 2DE in the native environment, such as "Native-IEF x SDS-PAGE" or "Native-IEF x Native-PAGE" by replacing the reagents. However, the basic proteins cannot be separated with Native-PAGE.
For additional resources on gel electrophoresis equipment and reagents, please visit our Electrophoresis Systems & Transfer Equipment resource hub.
Materials
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?